Letter F – Dictionary of Automotive Terms
- F
-
- Abbreviation for Fahrenheit.
- Abbreviation for Field
- Abbreviation for Field terminal
- Fabric body
- A simple form of lightweight bodywork in which a waterproof, cloth-backed material is stretched over a wooden framework popular around 1930 and still used later by DKW and even after WWII by Lloyd.
- Fabric fatigue
- A term used with tires where the fabric degrades and results in tire cord breakdown due to repeated flexing and heat.
- FAC
- Abbreviation for Freight assembly center which is a large service center that sorts, loads, routes and dispatches freight into the carrier’s system.
- Face
-
- To shave the outer edges of a bottom bracket shell or the upper and lower ends of a Head tube to make them parallel with one another and square to the tube’s centerline.
- To machine a flat surface perpendicular to the axis at rotation on a lathe.
- To remove metal from the end of a shaft or the face of a larger part, e.g., flywheel.
- The front, visible, or working surface of a part (such as a valve) or a tool (such as a hammer).
- Facelift
- Minor styling modifications made by the manufacturer to a car model which may be approaching the end of its useful life, intended to improve the appearance and thus boost sales with minimum cost, including such features as restyled headlights, larger tail lights, added trim, altered grille, and spoilers
- Facel Vega
-
A vehicle brand of which the 1954-64 V-8 models are milestone cars
- Face of weld
- The exposed surface of the Weld.
- Factory adjusted
- Something that is set by the manufacturer when the vehicle was built and is not intended to be changed
- Factory options
- Optional features which may be installed by the manufacturer upon request. Aftermarket options are those which are installed by a garage or consumer after the vehicle has been built and delivered to the selling dealership.
- Factory primer
- A Primer coat applied to new body panels in the factory for protection during storage, which in some cases has to be removed prior to painting because of paint compatibility problems
- Fading
-
- A loss of brightness or color in a paint finish.
- Brake fade
- Fahrenheit
- Thermometer on which the Boiling point of water is 212 degrees and the freezing point is 32 degrees above zero. To convert from Fahrenheit to Celsius, subtract 32 then multiply the result by 5 and divide by 9. To convert from Celsius to Fahrenheit, multiply by 9, then divide by 5. Now add 32 to the result.
- Fahrenheit scale
- On a Fahrenheit thermometer, under standard atmospheric pressure, boiling point of water is 212 degrees and freezing point is 32 degrees above zero.
- Failsafe system
- A system which remains safe even when part of it fails, such as a Dual-circuit brake system.
- Fair
-
- To add a Fairing to a body.
- A vehicle in restorable condition needing only minor work to get all components working
- Fairing
-
- A protective shell or enclosure at the front of a motorcycle which may house the headlights and signal lights. It is designed to improve the aerodynamic performance of the machine and/or provide rider comfort and protection from the elements. These range from simple Plexiglas® shields to complex, encompassing body panels.
- The plastic shield mounted on the front of a roof rack of a vehicle which is designed to reduce wind noise and improve fuel economy.
- Correcting or fairing up a ship’s lines or structural members; assembling the parts of ship so that they will be fair,that is, without kinks, bumps, or waves.
- FAIR Lanes
- Abbreviation for Fast And Intertwined Regular Lanes which are less congested lanes on a multi-lane road, for which a toll is charged. Drivers who take the alternative free lanes are offered credits which can be applied to future tolls, public transportation and public transportation parking facilities. In some cases these lanes can be used only by vehicles that have special electronic tags and there are no facilities to pay tolls by means of cash. FAIR lanes are a relatively new development.
- Fairlead
- A fitting through or over which a rope, line, etc., maybe led so as to change its direction without excessive friction.
- Fairwater
- Plate or casting used to preserve streamline flow of water past the hull structure or propeller hub.
- FAK
- Abbreviation for Freight of All Kinds describing mixed general freight in the back of a truck or trailer.
See
- Fall detection switch
- An electronic switch that shuts down the engine if the motorcycle is tilted at an angle which would indicate a fall.
- False air
- Any air leak that introduces unmeasured air into the intake system between the airflow meter and the intake valves is false
- False neutral
- When you fail to engage gears and the transmission behaves as though it is in neutral, even though it is not
- False flat
- An illusion where the operator or passengers in a motor vehicle or on a bicycle or motorcycle suppose that the road is flat, but in reality there is a slight climb.
- Family car
- A car suitable for transporting a family, usually a four-door sedan, hatchback, or station wagon. It is becoming more popular for families to obtain a Minivan instead of a station wagon.
- Fan
-
Fan
- A fan is a rotating device with curved blades like a propeller. The primary fan in a vehicle is generally located behind the radiator. Some electric fans may be placed in front of the radiator. It draws air through the radiator so that the coolant loses its heat through the fins of the radiator. It is especially needed when the vehicle is idling or moving slowly. When the vehicle moves quickly, there may be no need for the fan. In some cases, the fan is automatically disengaged under those circumstances. Non-electric fans may be activated by a Fan belt driven by the engine, while electric fans are powered by the electrical system independent of the engine itself.
- Other fans are located throughout the vehicle to push air from one location to another, especially for heating and ventilation.
- Radial or axial flow device used for moving or producing flow of gases.
- The pattern emitted by a paint spray gun.
- Fan belt
- A flexible rubber belt that connects various components in the engine compartment, i.e., Alternator, Water pump, emission controls, Power steering pump, and air conditioner compressor. Also called Drive belt or Serpentine belt
- Fan blade
- A part of the fan projecting at an angle from the central hub, which draws the air through the radiator
- Fan clutch
- A Viscous (fluid) drive coupling device connected to the center of the fan to permit variable engine fan speeds in relation to engine speeds. The clutch engages and disengages the fan according to the engine temperature through a thermostat
- Fan-cooled enclosure
- An electric motor housing that includes an integral fan to blow cooling air over the motor. It may be Totally enclosed or Explosion-proof
- Fan cooling
- A type of air cooling where a blower is responsible for transporting the amount of air required for the cooling of the engine past the cooling fins, which in turn dissipate the heat stored in them to the current of air flowing past them
- Fanning
- The use of air pressure through a spray gun to speed up the drying of Primer or paint — this is not recommended
- Farad
- Unit of electrical capacity; capacity of a condenser which, when charged with one coulomb of electricity, gives difference of potential of one volt.
- Faraday experiment
- Silver chloride absorbs ammonia when cool and releases it when heated. This is basis on which some absorption refrigerators operate.
- Farman
- A vehicle brand of which all 1920 – 1931 models with required application are classic cars.
- Farm gasoline
- Gasoline that has been mixed with an identifying dye (usually purple) and sold for less in order to help farmers. In most places where this is practiced, it is illegal to use farm gasoline in non-farm vehicles. Also called purple gas
- Farm out
- An action by a repair shop to send some repair work to a specialty shop. For instance you might bring your car to the shop for an engine tune-up and to replace a broken windshield. The shop can handle the tune-up, but will farm out the windshield repair to a glass shop.
- Farm Products cargo
- Truck content of unprocessed items which were grown in or produced from agricultural activity on a farm or in a garden, nursery, or orchard. Articles manufactured or processed from these commodities are not included in this category.
- Farm Tractor
- A low-speed high-torque vehicle used in farming. Typically with two small front wheels and two large rear wheels. Designed to pull other components in farming. In contrast with a Truck tractor
- Farm use
- Petroleum products sales for use on the farm including use in tractors, irrigation pumps, other agricultural machinery, etc.)
- FARS
- Abbreviation for Fatality Analysis Reporting System operated by the US NHTSA
- FAS
- Abbreviation for free alongside ship with the named port of shipment. The seller fulfills his obligation to deliver when the goods have been placed alongside the vessel on the quay or in lighters at the named port of shipment. This means that the buyer has to bear all costs and risks of loss or of damage to the goods from that moment. The FAS term requires the buyer to clear the goods for export.
- Fascia
- Also spelled facia.
- A front protective panel usually located below the bumper.
- A British term for the instrument panel.
- Fast
- A word used to describe the angle or tilt of a windshield or backlight (i.e., rear window). The ‘faster’ the glass, the more nearly horizontal it is. Its ‘fastness’ is measured between zero degrees (horizontal) and 90° (vertical); i.e. a 57° windshield is faster than one standing more upright at 80°.
See
- Fastback
-
Fastback
A design of car where the roof gently slopes to the rear end of the car. Any automobile with a long, moderately curving, downward slope to the rear of the roof. This body style relates to an interest in streamlining and aerodynamics and has gone in and out of fashion at various times. Some (Mustangs for one) have grown quite popular. Others have tended to turn customers off. Certain fastbacks are, technically, two-door sedans or pillared coupes. Four-door fastbacks have also been produced. Many of these (such as Buick’s late 1970s four-door Century sedan) lacked sales appeal. Fastbacks may or may not have a rear-opening hatch.
- Fast charger
- A battery charger which can charge a battery at a rate of 40 amps or more, used by garages and battery suppliers
- Fastener
- A device used to attach one part or assembly to another (nut and bolt, screw, nail, staples, rivet, etc.).
- Fastener Shear Index
- The relative measurement of shear resistance of a pallet fastener.
- Fast food freezing
- Method that uses liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide to turn fresh food into long lasting frozen food. It is often referred to as cryogenic food freezing and freeze drying.
- Fast idle
- When the engine is cold, it needs to run faster to keep it from stalling. A cam on the carburetor forces the Throttle open a little more when the Choke is engaged.
- Fast idle cam
- A cam in a carburetor which opens the throttle slightly when the choke is brought into operation, either automatically or mechanically
- Fast idle screw
- A screw on a carburetor for adjusting the speed of the fast idle
- Fast idle solenoid
- A Solenoid operating in conjunction with an automatic choke to open the throttle slightly when the choke is in operation
- Fast lane
- The outside lane (far left lane in North America, etc. or the far right lane in Britain, Australia, etc.). Also called the passing lane
- FAS value
- Abbreviation for Free alongside ship value. The value of a commodity at the port of exportation, generally including the purchase price plus all charges incurred in placing the commodity alongside the carrier at the port of exportation in the country of exportation.
- Fatality Analysis Reporting System
- (FARS) operated by the US NHTSA
- Fathom
- A measure of length, equivalent to 6 linear feet, used for depths of water and lengths of anchor chain. 120 fathoms = 1 cable. 6,085 feet = 1 nautical mile.
- Fathometer
- A device to measure the depth of water, by timing the travel of a sound wave from the ship to the ocean bottom and return.
- Fatigue
- A condition of a material, especially a metal, causing loss of elasticity and tendency to fracture after long or repeated stress, even though the stress may be less than that which would cause failure under static conditions.
- Fatigue life
-
- When a metal component is subjected to repeated bending or service action it will eventually break. The number of bends is its fatigue life.
- The number of specified load reversals at which a metal component will fail.
- Fatigue limit
- The maximum stress that a material can endure for an infinite number of stress cycles without breaking
- Fatigue strength
-
- The maximum stress that a material can endure for a given time without breaking
- The stress to which a metal can be subjected for a specified number of cyclic changes of stress.
- The endurance of a fastener showing the load it can accept without breaking under repeated load cycles.
- Fatigue test
- A test on a material to determine the range of stress it will stand without failing, by subjecting it to rapidly varying stresses to establish its fatigue limit
- Fat load
- Trucker slang for overload, carrying more weight than local state law allows as in ‘Better not be running at fat load, cause the coops are open and checking ground pressure this morning.’
- Fault
- A defect which is either inherent in the vehicle as built (manufacturing fault) or which occurs during running.
- Fault diagnosis
- The tracing of faults or error codes which can be determined by the in-built diagnostic system and an engine analyzer
- Fault memory
- A part of the electronic control unit and of the diagnostic system that stores error codes to assist the mechanic in diagnosing problems.
- Fault reader
- A device used in conjunction with the vehicle’s diagnostic system, providing a read-out of status of the various components
- Faux cabriolet
- A fixed head coupe made to resemble a cabriolet.
- Faying surface
- The inner mating or contacting surfaces of a joint; common area of two surfaces that are bonded together with an adhesive
- FBC
- Abbreviation for Feedback carburetor
- FBP
- Abbreviation for Final Boiling Point — The highest temperature indicated on the thermometer inserted in the flask during a standard laboratory distillation. This is generally the temperature at which no more vapor can be driven over into the condensing apparatus.
- FC
- Abbreviation for Fan Control
- FCA
-
- Abbreviation for Fuel Control Assembly (Chrysler)
- Abbreviation for Free Carrier with the named place. The seller fulfills his obligation to deliver when he has handed over the goods, cleared for export, into the charge of the carrier named by the buyer at the named place or point.
- FCCC
- Abbreviation for Framework Convention on Climate Change
- FCS
-
- Abbreviation for Feedback control system
- Abbreviation for fuel control solenoid
- FDBK
- Abbreviation for Feedback
- FE analysis
- Abbreviation for Finite-Element Analysis
- Fease out
- To determine the feasibility or manufacturability of a design. This is usually an engineering function.
- Feasibility Study
- A study about a project’s feasibility. The study addresses issues including the project’s benefits, costs, effectiveness, alternatives considered, analysis of alternative selection, environmental effects, public opinions, and other factors.
- Featherbed frame
- Famous Norton motorcycle frame design by the McCandless brothers. It was introduced in 1950 and was given its name by factory rider Harold Daniell
- Feather edge
-
See
- Feather-edge
-
- The tapered edge of the paint where it meets the metal. The edges should be tapered or slanted so that no edge will be felt when a finger is passed over it.
- To sand the edges of a repaired area until they merge into the surrounding paintwork.
- Feathering
-
- A type of tire wear in which the tread is worn down to a very thin edge
- The application of gentle pressure on the throttle or brake pedal
- Feather key
-
- A key with parallel faces whose ends may be round or square. It usually fits into a groove on a shaft and in a mating hole to secure the shaft in place.
- A parallel key fastened in either the shaft or in the hub of a member sliding on it. When fastened in the shaft, it must be long enough to hold or drive the sliding member in any of its positions on the shaft. When in the sliding member the key need only be as long as the hub.
- FEBIAC
- Abbreviation for Fédération Belge des Industries de L’Automobile et du Cycle ‘réunies’ (Belgium)
- Federal Energy Regulatory Commission
- (FERC) The Federal agency with jurisdiction over interstate electricity sales, wholesale electric rates, hydroelectric licensing, natural gas pricing, oil pipeline rates, and gas pipeline certification. FERC is an independent regulatory agency within the Department of Energy and is the successor to the Federal Power Commission.
- Federal engine
- An American engine which meets US Federal emission standards and certified by the EPA for use in any state except California
- Federal Highway Administration
- (FHWA) The U.S. federal agency responsible for the administration of federal highway funds. FHWA coordinates highway transportation programs in cooperation with states and other partners to enhance the country’s safety, economic vitality, quality of life, and the environment. Major program areas include the Federal-Aid Highway Program, which provides federal financial assistance to the States to construct and improve the National Highway System, urban and rural roads, and bridges. This program provides funds for general improvements and development of safe highways and roads. The Federal Lands Highway Program provides access to and within national forests, national parks, Indian reservations and other public lands by preparing plans and contracts, supervising construction facilities, and conducting bridge inspections and surveys.
- Federal Power Commission
- (FPC) The predecessor agency of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission. The Federal Power Commission was created by an Act of Congress under the Federal Water Power Act on June 10, 1920. It was charged originally with regulating the electric power and natural gas industries. It was abolished on September 30, 1977, when the Department of Energy was created. Its functions were divided between the Department of Energy and the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission, an independent regulatory agency.
- Federal side impact standard
- Effective with the 1997 model year, all passenger cars are required to comply with Standard 214, side impact protection, as defined in the Code of Federal Regulations. Simply put, the entire structure, floor to roof, of all cars must now be reinforced according to strict regulations. Interestingly, this standard does not yet apply to light trucks (e.g., Minivans, compact Pickups, SUVs).
- Federal Test Procedure
- (FTP) Test cycle(s) used in the U.S. for emission testing and certification of engines and vehicles. The chassis dynamometer cycle for light duty vehicle testing is commonly referred to as FTP-75. The engine dynamometer cycle for testing of heavy-duty (HD) engines is known as HD FTP, or FTP Transient cycle.
- Federal version
- A vehicle that complies with U.S. emission standards which are less restrictive than the standards in California. Also called a 49-state car.
- Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile
- (FIA) The international umbrella motoring organization to which national motoring organizations are affiliated and racing is sanctioned. This includes FIA Formula One World Championship (the world’s premier racing series also called Formula One racing or F1), International Sports Car Championship (BPR), International Touring Car Championship, and through the Concorde Agreement (agreement to operate racing series under the FIA’s guidelines and rules) for participating country’s car clubs. Events take place worldwide. The current president is Max Mosley and the V.P. of Marketing is Bernie Eccelestone who controls the series.
- Fédération Internationale du Sport Automobile
- (FISA) The international governing body of motor sport
- Feedback
-
- The return of part of the output of a system to the input. Negative feedback causes self-adjustment of the system and therefore Stability. Positive feedback causes instability.
See
- The information that a computer-controlled fuel system returns. The sensor measures the oxygen content of the engine’s exhaust in order to keep the fuel-air ratio very close to the ideal proportion for combustion. Such tight control of the fuel-air ratio is required for the proper operation of three-way catalysts.
- Information on current operation of a system or device used by the control system to modify future operation.
- In electrical motors and controls, it is the voltage information received by a feedback circuit. Depending on a predetermined potentiometer setting, an electric motor control can correct the voltage to deliver appropriate speed and/or torque
- The return of part of the output of a system to the input. Negative feedback causes self-adjustment of the system and therefore Stability. Positive feedback causes instability.
- Feedback carburetor
- (FBC) A carburetor regulated by a closed loop system (an oxygen sensor, various other sensors, a computer, a duty-cycle Solenoid or solenoid-controlled valve and a catalytic converter) providing and adjusting the air/fuel mixture quality to operate a catalytic converter
- Feedback carburetor actuator
- A computer-controlled stepper motor that varies the carburetor air/fuel mixture
- Feedback control system
- (FCS)
- A computer-controlled fuel system employing a stepper motor or a dithering Solenoid that controls air-fuel mixture by bleeding precise amounts of air (determined by the computer) into the main and idle system of the carburetor
- Control system that is constantly correcting the condition. Also called a closed loop system.
- Feedback potentiometer
- A variable resistance device which monitors the position of the shaft to which it is affixed and reports the position to the control head
- Feed check valve
- A one-way control valve positioned between the supply pump and the storage container.
- Feeder
- In intermodal moves, a pickup/delivery vehicle or ship.
See
- Feedstock
- Any material converted to another form of fuel or energy product. For example, corn starch can be used as a feedstock for ethanol production.
- Feed the bears
- Trucker slang for receive a ticket as in ‘Looks like that chicken hauler likes to feed the bears.’
- Feel
- The detection of the operation of a vehicle and its components. Brake feel involves detecting how effectively the brakes work; Road feel conveys to the driver the way the suspension responds to the road.
- Feeler blade
- A thin blade of spring steel of an exact thickness for measuring small gaps or clearances between parts, usually made in sets of various thicknesses pinned together at one end to form a feeler gauge
- Feeler gauge
-
Feeler gauge
A thin strip or blade of hardened steel, ground to an exact thickness, that is used to check Clearances between two parts. Thicknesses increase by 0.001 inch.
- Feeler strip
- A metal strip of a specific thickness from which single feeler blades can be cut, appropriate when frequent measuring is required, to avoid using worn blades
- FEMA
-
- Abbreviation for The Federation of European Motorcyclists Associations on http://www.fema.ridersrights.org/
- Abbreviation for Federal Emergency Management Agency
- Female
- A fitting inside another part. Usually where two parts form a connection of some kind, the female part is the socket or hole into which another piece is inserted.
- Female end
- The receptacle into which the Male end is inserted.
- Female thread
- The internal thread on fittings, valves, machine bodies, etc. like that within a nut. Male threads are found on bolts and screws.
- Fencer’s mask
- The term used to describe a type of radiator grille design from the 1930’s which resembled the mask of a fencer with its shape and fine weave of the grille.
- Fender
-
- A covering over the wheels to prevent mud from splattering. The British term for this part is wing.
- British term for bumper.
- A portable device to protect a ship when bumping a pier; sometimes made of wood, rope, etc.; permanently installed extension which protects the hull of a ship in docking.
- Fender arch
- A smoothly shaped, rounded widening of the wheel arch area to extend the wheel arch further from the body and allow wider tires to be installed. The British term is wing arch
- Fender beading
- A strip of ornamental molding used to cover the seam between two adjacent body panels, such as the fender and the body. In most cases, this strip is chromed and permanently attached (i.e., it is destroyed when it is removed and cannot be reused).
- Fender bender
- A Car accident in which only minor damage is done to body panels.
- Fender bumping hammer
- A body hammer with a one-sided, fairly long head that is lightly curved and terminates in a rounded section; it is used to reach fender curves from the inside
- Fender crown
- A domed area of the hood, fenders or roof. Also a subtle rise or convexity in a surface to make it look straight or flat instead of sunken.
- Fender extension
- A smaller panel in the bottom front area of the front fender that extends the fender toward the front panel and the Wheel housing
- Fender landing section
- A horizontal flange at the top of the Flitch plates that provides the seating for the fenders; in most cases, it also includes the mounting threads or spot-welds for attaching the fenders
- Fender mirror
- A rear-view mirror mounted on the fender. It used to be a common placement, but now the outside mirror is mounted on the door.
- Fender mounting
- The top flange of the sidewalls in the engine compartment and its vertical extensions at the front and rear; the fender is welded or bolted to this edge along its entire length
- Fender punch
- A hole punch with a specially shaped head to fit over awkward fender panels, rain gutters, and wheel arches

- Fender skirt
- A panel or plate usually of sheetmetal designed to cover a portion of the rear fender wheel opening or wheel arch. It was available either as stock equipment, as an optional extra, or as an aftermarket item.
- Fender splash apron
- A panel on the inside of the fender to prevent splashing water from reaching certain areas of the fender, Wheel housing, and A-post; as opposed to wheel house panels, it is usually flat and mounted in an upright position behind the front wheels
- Fender strengthening buttress
- A horizontally closed section of triangular shape in the upper rear edge of the inner fender area that adds rigidity to this area
- Fender support bracket
- A sheet metal brace used to attach the bottom edge of the fender to the body, to keep it from flexing and vibrating
- Fender valance
- A front-fender extension hanging down behind the wheel, intended to hide the undersurface and chassis.
- FERC
- Abbreviation for Federal Energy Regulatory Commission — The federal agency that regulates interstate gas pipelines and interstate gas sales under the Natural Gas Act. Successor to the Federal Power Commission, the FERC is considered an independent regulatory agency responsible primarily to Congress, but it is housed in the Department of Energy.
- FERC guidelines
- A compilation of the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s enabling statutes; procedural and program regulations; and orders, opinions, and decisions.
- FERC Order 380
- Issued in 1983, it invalidated contract requirements that a gas utility pay a pipeline for a certain amount of gas even if it could not take the gas. This paved the way for utilities to buy gas directly from producers and marketing companies.
- FERC Order 436
- Issued in April of 1985, it set up a voluntary open-access transportation program that allowed pipelines to offer transportation service not linked to gas sales service, making it easier for utilities and gas customers to purchase gas directly from producers and marketing companies and have it transported by pipelines.
- FERC Order 451
- Issued in 1987, it provided the opportunity for sellers of gas from older wells to receive a more market-sensitive price.
- FERC Order 500
- Issued in late 1989, it was an addendum to FERC Order 436 and provided mechanisms for settling certain contract liabilities incurred by pipelines that could not take all of the gas they had ordered from producers.
- Ferguson four-wheel drive
- A transmission system in which power is distributed through a special Viscous coupling differential, 37% to the front wheels and 63% to the rear wheels
- Fermentation
- The enzymatic transformation by microorganisms of organic compounds such as sugars. It is usually accompanied by the evolution of gas, as in the fermentation of glucose into ethanol and CO2.
- Ferrari
-
A vehicle brand of which the V-12 (All Front Engined) (1947-70) models are milestone cars.
- Ferritic
- Something containing less than 5% of stainless fasteners, mainly type 430, it is magnetic and not hardenable by heat treatment. Though containing no nickel, ferritic stainless has a high chromium content providing greater corrosion resistance than martensitic stainless but much less than austenitic. It is mainly used by the automotive and building industries for decorative trim, architectural hardware, handrails, moldings on various products.
- Ferrous metal
- Metal containing iron or steel. Non-ferrous metals are Aluminum Alloys, Brass, copper, or magnesium.
- Ferrule
- A cap (cylindrical metal piece with a hole at each end) attached to the end of the cable outer Housing to protect the cable housing from fraying.
- Festoon bulb
-
Festoon bulb
A light bulb in the form of a small glass tube with caps at each end providing the contacts
- FF
- Abbreviation for Flexible Fuel
- FF headlight
- A free-form headlight using a free-shape reflector
- FFÖ
- Abbreviation for Fachverband der Fahrzeugindustrie Österreichs (Austria)
- FFOT
- Abbreviation for Ford fixed orifice tube system
FGD
Abbreviation for flue-gas desulfurization
- FHC
- Abbreviation for fixed head coupe, a hardtop coupe (closed coupe).
- F-head engine
-
F-head engine
An engine having one valve in the head and the other in the Block. The position of the valves create an F shape in combination with the combustion chambers. Compare L-head engine where both valves are in the block and none in the head. Compare the I-head engine where both valves are in the head and none in the block.
See
- FHP
- Abbreviation for Friction horsepower
- FHWA
- Abbreviation for Federal Highway Administration which is the U.S. federal agency of the department of transportation responsible for the administration of federal highway funds. FHWA coordinates highway transportation programs in cooperation with states and other partners to enhance the country’s safety, economic vitality, quality of life, and the environment. Major program areas include the Federal-Aid Highway Program, which provides federal financial assistance to the States to construct and improve the National Highway System, urban and rural roads, and bridges. This program provides funds for general improvements and development of safe highways and roads. The Federal Lands Highway Program provides access to and within national forests, national parks, Indian reservations and other public lands by preparing plans and contracts, supervising construction facilities, and conducting bridge inspections and surveys.
- FI
- Abbreviation for fuel injection.
- FIA
- Abbreviation for Fédération Internationale de l’Automobile — An international umbrella motoring organization to which national motoring organizations are affiliated
- Fiat
-
A vehicle brand of which the 1925-1948 models with required application are classic cars.
- Fiberglass
- A mixture of glass fibers and resin that when cured (hardened) produces a very light and strong material. It is used to build boats, car bodies, repair damaged areas, etc. It can also be spelled Fibreglass. Also called glass reinforced plastic.
- Fibreglass
- A mixture of glass fibres and resin that when cured (hardened) produces a very light and strong material. It is used to build boats, car bodies, repair damaged areas, etc. It can also be spelled Fiberglass.
- Fiberglass body
- A body shell which is molded in one piece from fiberglass and has the advantage of lightweight and freedom from corrosion
- Fiberglass mat
- A layer of chopped but irregular individual fiberglass strands dressed with a chemical to hold them loosely together, which when a resin is applied hardens into a strong material for repairing holes, e.g. in car bodies
- Fiber optics
- The transfer of light through glass fibers. Cadillac, for instance, transfers the light of the headlight or taillight through fiber optics showing that the lights are actually on; rather than just an electrical connection which shows that the indicator light works.
- Fiber reinforced plastic
- (FRP) Continuous mat or woven fibers impregnated with plastic resins to form a lightweight but extremely strong solid. These plastics are stronger per pound than steel. Commonly used fibers are aramid (kevlar), carbon fiber, nomex, and glass. These fibers are used alternatively to provide various levels of strength and weight.
- Field
-
- A particular body of interest or expertise.
- The area covered or filled with an electric, magnetic, or gravitational force.
- Field coil
-
- Insulated wire wrapped around an iron or steel core. When electrical current flows through the wire, a strong magnetic force field is built up.
- An electromagnet used in a dc generator or ac electromagnet alternator to produce a magnetic field.
- Field intensity
- The force acting on a unit electric charge or unit magnetic pole placed at a given point.
- Field pole
- Part of Stator of motor which concentrates magnetic field of Field winding.
- Field terminal
- (F) The input terminal on a Generator
- Field weakening
- The introduction of resistance in series with the shunt-wound field of an electric motor to reduce the voltage and current that weakens the strength of the magnetic field and thereby increases the motor speed
- Field winding
- That part which produces a constant-strength magnetic field in an electric motor or Generator, the field core being on the Stator or the rotor depending on the type of motor or Generator
- Fierceness
- The tendency of a clutch to engage suddenly so that it is difficult to proceed smoothly from a stop
- Fiesta
- The 1953 Oldsmobile Fiesta is a milestone car.
- FIEV
- Abbreviation for Fédération des Industries des Equipements pour Véhicules (i.e., The French Vehicle Equipment Industries Association)
- FIFO
- Abbreviation for First In, First Out to describe an inventory allocation method whereby the first product stored is the first product that is used or allocated for the fulfillment of orders. Contrast FILO
- Fifth wheel
-
- A wheel that is temporarily attached to a vehicle to test the accuracy of the Speedometer, etc.
- A recreational trailer which has its tongue attached to the bed of a truck.
- A coupling device attached to a tractor or dolly which supports the front of a semitrailer and locks it to the tractor or dolly. The fifth wheel’s center is designed to accept a trailer’s kingpin, around which the trailer and tractor or dolly pivot in turns.
- Fifth-wheel travel trailer
-
Fifth-wheel travel trailer
A recreational trailer which is towed by a pickup truck. The tongue of the trailer fits into the bed of the truck. Like a travel trailer, it comes with all the amenities of home. The master bedroom is over the truck bed. They have an extension on the front of the box that extends over the tow vehicle and a horizontal plate that looks like a wheel (hence the name fifth wheel) that rests on the tow vehicle for support. This hitch arrangement requires special equipment on the tow vehicle. The trailer is outfitted with a fifth-wheel hitch (also known as a gooseneck hitch). The hitch arrangement makes towing easier by placing the trailer load in the center of the tow vehicle instead of behind it. The extension on the front of the box also serves as a bedroom in most fifth wheels. Fifth-wheel trailers usually provide cooking facilities, a refrigerator, heater, air conditioner, a self-contained toilet, a shower, water tanks (fresh water, grey water, black water), faucets, sinks, a LP (propane) gas supply, and a separate 100-125 volt electrical system. Some have built-in washer and dryer, slide-out room extension. They can sleep up to six people. Prices range from $15,000 to $150,000.
Fifth-wheel trailer
- Fifty-fifty power split
- An arrangement in a four-wheel drive transmission where equal amounts of power are delivered to the front and rear wheels
- Filament
- A fine wire inside a light Bulb that heats to incandescence when current passes through it. The filament produces the light.
- File
-
File
- A flat or rounded tool with a rough surface of hardened steel. When it is rubbed against metal, it removes small bits of metal leading to a smaller amount of base metal.
- The action of removing metal by using a file.
- File card brush
- A brush with angled wire bristles for cleaning between the teeth on a file or the threads on a bolt.
- Filler
-
- Paste usually with a polyester base which, when mixed with a hardener, forms a surface which can be sanded smooth and is suitable for repairs to dented or rusted bodywork. Also called filler paste.
- A Primer filler.
- An inert material added to paper, resins, and other substances to modify their properties and improve quality.
- An opening through which some liquid can be poured (i.e., oil or gasoline).
- Substances added to friction materials to obtain specific performance characteristics.
- Filler door
- A hinged door (usually less than six inches square and painted the body color) which covers the gas cap and filler neck on some models.
- Filler neck
- A funnel shaped part which is connected to the main container (gas tank, radiator, windshield washer reservoir, etc.) and is usually covered with a cap.
See
- Filler port
- The passage through which brake fluid flows from the reservoir to the cylinder bore, refilling the low pressure ahead of the cup on the return stroke. Also called an inlet port or intake port.
See
- Filler rod
- A metal wire that is melted and added to the welding puddle to produce the necessary increase in bead thickness.
See
- Fillet
-
- A round Joint between two parts connected at an angle.
- Weld metal in the internal vertex, or corner, of the angle formed by two pieces of metal, giving the joint additional strength to withstand unusual stresses.
- A concave, transitional surface that fills, mates, or blends two intersecting surfaces.
- Fillet weld
- Metal fused into a comer formed by two pieces of metal whose welded surfaces are approximately 90° to each other.
- Filling
- Repairing of holes or dents in bodywork with filler paste or Body lead
- Filling station
- A British term for a Gas station
- Fillister-head machine screw
-
Fillister-head machine screw
A machine screw with a head that has a flat bottom to fit flush with the surface of the material and has a deep rounded head
- Fillister screw
- A Set screw with a deep rounded head
- Fill plug
- A small screw-in plug in the steering box or similar, which is removed for topping up with oil.
- Fill up
-
- To put in the full amount of fuel as in ‘Fill up the gas tank, I’m down to a quarter of a tank’. Often said, Fill ‘er up or Fill her up.
- The amount needed to make a full tank as in ‘I need a fill up’.
- Film strength
- The ability of a liquid like oil to withstand pressure and to keep moving parts from making contact with each other.
- FILO
- First-in, last-out system of inventory. See FIFO
- Filter
-
- A device designed to remove foreign substances or particles from air, oil, gasoline, water, etc.
- A device used either with the drier or as a separate unit to remove foreign material (contaminants) from the refrigerant
See
- Air cleaner
- Air filter
- Analog Filter
- Band-stop Filter
- Band-pass Filter
- Bypass filter
- Canister air filter
- Centrifugal force air filter
- Centrifugal oil filter
- Ceramic filter
- Ceton Filter
- Charcoal filter
- Cuno filter
- Diesel particulate filter
- Electrostatic Filter
- fuel filter
- Full-flow oil filter
- fuel Filter
- Gas filter
- in-line fuel filter
- integral fuel filter
- Micro oil filter
- Oil filter
- Oil filter cartridge
- Oil filter housing
- Oil filter bypass valve
- Oil filter wrench
- Partial flow filter
- Pod filter
- Sock filter
- Surface-type filter
- Vacuum filter
- Filter cartridge
- The replaceable porous part of some oil filters and air filters; but often refers to the whole filter. Also called filter element.
- Filter element
- The replaceable porous part of some oil filters and air filters; but often refers to the whole filter. Also called filter cartridge.
- Filter screen
- A piece of wire mesh in a pipe or surrounding an air filter which is designed to collect dirt and foreign matter
- Filter wrench
-
Filter wrench
An oil filter wrench for removing the Oil filter.
- FIM
- Abbreviation for Fédération Internationale Motorcylistes, the governing body of international motorcycle sports
- Fin
-
- A thin metal object projecting from a surface and is used to dissipate heat. It is found on radiators and air-cooled engines.
- Wings and airfoils used to improve a vehicle’s aerodynamics, stability, or possibly aesthetics.
- A thin projecting rib.
- Final Boiling Point
- (FBP)
- The temperature at which a substance starts to boil is referred to as the Initial Boiling Point (IBP), and the temperature at which it boil off completely is referred to as the Final Boiling Point (FBP).
- The highest temperature indicated on the thermometer inserted in the flask during a standard laboratory distillation. This is generally the temperature at which no more vapor can be driven over into the condensing apparatus.
- Final drive
-
- This is the end of the drive train before power is transmitted to the wheels. In a typical car, the engine (or electric motor) transmits its power through some sort of clutch into a transmission. Then the power is transmitted to differential gears that adjust the engine speed to the most efficient use intended. These final drive differential gears are either at the front axle or rear axle, depending on the vehicle’s layout. A typical family car or one intended for high speeds will have a low numerical ratio, to give it speed and good fuel efficiency. A truck or performance car is likely to have a high numerical ratio for better pulling power or for better acceleration
- Chains and sprockets or shafts and gears used to connect the transmission output shaft to the rear wheel.
- Final drive gear
- The last gear in a Drivetrain before the driven wheels. Usually it is in the differential.
- Final drive ratio
- This is the ratio that describes the difference between the number of times the driveshaft must turn before the axle shaft turns once. In a final drive ratio of 3.551, for example, the driveshaft must turn 3.55 times before the axle will turn once. The number of teeth on the Ring and pinion gears determine the ratio. In most instances, the ratio is not a simple number like 3.001 because the same teeth on the drive and driven gears would always meet and cause wear.
- Final purchase price
- This price is equivalent to the amount you would pay for the vehicle if you were buying or financing rather than leasing. The final purchase price does not include any down payment by the lessee.
- Finance and control
- Ownership of company (i.e., Canadian, U.S., Japanese, German, etc.); public or private; capital investments Buildings, machinery and equipment, Tooling programs.
- Fine
-
- Something that is made of very small particles.
- The position of threads on a bolt or nut that are very close together.
- Fine-structure constant
- A dimensionless constant, equal to 7.297351 x 10-3 (approximately 1/137), given by 2π times the square of the electron charge, divided by the product of the speed of light and Planck’s constant.
- Finger tight
- The torque required when securing something without the use of a wrench; but using only one’s fingers.
- Finish
-
- The final coat of paint applied to a vehicle.
See
- The overall look of a vehicle so that the paint, for instance, is evenly applied, there are no bare spots, etc. Usually this word is used in the expression Fit and finish.
- Surface refinement as in smooth finish.
- The final coat of paint applied to a vehicle.
- Finish coat
- The final color Coat applied to a vehicle.
- Finished leaded gasoline
- Gasoline that contains more than 0.05 gram of lead per gallon or more than 0.005 gram of phosphorus per gallon. Premium and regular grades are included, depending on the octane rating. Includes leaded gasohol. Blendstock is excluded until blending has been completed. Alcohol that is to be used in the blending of gasohol is also excluded.
- Finish hammer
- A pounding device used for detail work in shaping a panel after it has been brought approximately into the right shape.
- Finishing enamel
- The paint used as the top coat of a painting system — usually before a clear coat is applied. Also called finishing paint.
- Finishing paint
- The paint used as the top coat of a painting system — usually before a clear coat is applied. Also called finishing enamel.
- Finish restorer
- A polish or rubbing compound with very slight abrasive which is used to remove an oxidized paint surface to bring back its original luster.
- Finishing stone
- A fine grain stone used at the completion of the honing process to give a smooth surface.
- Finite-element analysis
- A reduction of a complex structure to its basic component parts so that these can be studied in a computer, especially in a CAD process. Also called FE analysis
- Fin neck carriage bolt
- A plain, circular, oval head bolt with two fins or protrusions located below the head that fits into corresponding notches to prevent rotation.
- Finning
- An arrangement of fins on a surface to aid cooling by improving the heat transfer rate, typically found on air-cooled engines
- Fins
- A series of blades such as are found in the internal design of the torque converter. To create mechanical torque from hydraulic pressure, oil is forced under pressure through the torque converter. The inside of the converter is made up of layers of steel fins which zigzag in direction and vary in size. First the fins are large but as the layers go on, the fins decrease in size. This design generates greater hydraulic pressure as the oil passes through the converter, the strong flow of oil creates a fluid coupling which operates like a clutch, driving the wheels.
See
- Fire appliance
- A British term for Fire engine
- Fireball combustion chamber
- A combustion chamber design developed by the Swiss engineer May and introduced on Jaguar’s V-12 engine in 1981

- Fire engine
- A vehicle built on a special truck chassis equipped with fire-fighting items such as ladders, pumps, hoses, etc.
- Firenza
-
A model of automobile manufactured by the Oldsmobile division of General Motors from 1982-88
- Fire extinguisher
- A cylinder filled with a powder, foam, or liquid which can be sprayed on a fire to put it out.
- Fire point
-
- The temperature at which the vapor continues to burn.
- The lowest temperature at which an oil vaporizes rapidly enough to burn for at least 5 seconds after ignition, under standard conditions.
See
- Firewall
- The metal partition between the passenger compartment and the engine compartment. On front engine vehicles, it is located below the windshield; but on rear engine vehicles, it is located below the backlight (i.e., back window). It protects the driver and passengers from engine fires, noise, and fumes. The British term is bulkhead.
- Firing order
- The staggered sequence or order in which the cylinders must be fired (expressed as a series of numbers such as 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4, etc.). It differs from the cylinder sequence which starts with cylinder number one and goes to the last cylinder (expressed for example as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6). The sequential firing order distributes the shock of combustion evenly and reduces engine vibrations.
- Firm
- A business or institution comprising sole proprietorships, partnerships, companies and other forms of organizations.
- First
- The lowest gear in a transmission. In a bicycle, it is the gear ratio where the drive sprocket is the smallest and the driven sprocket is the largest. This gear is the best for starting from a stop or going up a hill.
- First-aid kit
- A box containing bandages, antiseptic ointment, and other basic medical requirements for treating injuries.
- First gear
- The lowest gear in a transmission. In a bicycle, it is the gear ratio where the drive sprocket is the smallest and the driven sprocket is the largest. This gear is the best for starting from a stop or going up a hill.
- First law of thermodynamics
- The natural law that states energy can neither be created nor destroyed, and that energy can only be converted into another form.
- FISA
- Abbreviation for Fédération Internationale du Sport Automobile which is the governing body of motor sport
- Fish eye
- A small pit that forms in the Finish coat of paint, usually due to insufficient or improper cleaning of the old Coat.
- Fish eyes
- Small pits that form in the Finish coat of paint, usually due to insufficient or improper cleaning of the old Coat.
- Fishy back
- Transporting motor carrier trailers and containers by ship.
- Fit
-
- Contact area between two parts.
- The way in which two parts come together.
- To attach or put into place.
- The range of tightness which may result from the application of a specific combination of allowances and tolerances in the design of mating parts.
- Normally referring to threads, fit is a measure for the tightness of mating parts.
- Fit and finish
- The evaluative standard of a vehicle’s cosmetics. Good fit and finish means all the body panels and Trim are evenly spaced, aligned, and secure. The paint is evenly applied with no bubbles or pit marks.
- Five-axis milling machine
- A milling machine that can be programmed not only to follow the conventional X-Y-Z axes but which also keeps the milling head perpendicular (normal) to the surface at all times. These additional two ‘axes’ are programmed into the computer as front-to-rear and side-to-side instructions. (The concept of five actual axes is misleading; there are still only three).
- Five-door
- Body design typical of station wagons and most hatchbacks, with four side doors and a tailgate.
- Five-door hatchback
-
Five-door hatchback
Essentially unknown among domestic models in the mid-1970s, the four-door hatchback became a popular model as cars grew smaller and front-wheel-drive versions appeared. Styling was similar to the original two-door hatchback, except for two more doors. Luggage was carried in the back of the car itself, loaded through the hatch opening, not in a separate trunk.
- Five-link rear suspension
- Independent rear suspension layout also used on live rear axles, in which each wheel is guided by two trailing links, two transverse links and a common track rod
- Fivers
- Colloquial term for Fifth-wheel travel trailer
- Five-speed transmission
- A manual transmission with five forward gears. Generally the fifth gear is an Overdrive to allow the wheels to turn faster than the engine.
- Five-valve head
- A cylinder head which has five valves per cylinder, usually three intake valves and two exhaust valves
- Fixe
- A bicycle (or its transmission) which does not allow coasting. The rear sprocket is ‘fixed’ to the wheel and driven by a chain so that each rotation of the crank moves the wheel forward.
- Fixed anchor
- A non-adjustable anchor pin. It can be riveted or welded to the backing plate, or it can pass through the backing plate and attach to a part of the suspension system
- Fixed-anchor grind
- A variation of Undersize grinding that compensates for the size and location of a fixed shoe anchor.
- Fixed caliper
- A disc brake caliper rigidly mounted to the steering knuckle or spindle or control arm. It can have one or two pistons on each side of the disc and does not float or slide.
- Fixed-caliper disc brake
- A disc brake with a caliper which cannot move, the caliper consisting of two halves which are bolted together and contain at least one cylinder and piston each
- Fixed-choke carburetor
- A carburetor where the choke tube or venturi is of predetermined size
- Fixed cup
- The right-hand cup of the bottom bracket of a bicycle, ordinarily not loosened or removed during bottom bracket disassembly.
See
- Fixed drive
- A power transmission without differential action at the driven axle or between the driven axles in a four-wheel drive layout
- Fixed gear
- A Cog attached to a hub without a freewheel; it always turns as fast as the bicycle’s wheel so that you cannot coast.
- Fixed head
-
- A non-removable cylinder head cast in one piece with the cylinder block. These heads were used in early automobile engines and, more recently, in some motorcycle engines.
- A British term for a solid non-removable roof, or coupe.
- Fixed idle-air bypass
- Some Rochester Quadrajet carburetors have idle air passages from the air horn to a point just below the throttle plates. Extra air through these passages allows the throttle plates to be more closed at idle, reducing the signal applied to the discharge nozzles for the main metering circuit and eliminating nozzle drip at idle
- Fixed-jet carburetor
- This is the most common type of carburetor in which the jets and choke are of a predetermined size. The opposite is a Variable-jet carburetor
- Fixed-mast antenna
- Automobiles employ three main types of radio antennas.
- Wires embedded in the glass of the windshield
- Power operated staff which rises from the surface of the sheet metal when the radio is turned on, but is lowered almost flush when the radio is turned off. It is usually made up of several sections which telescope together. See Power antenna
- A one-piece flexible rod or shorter stiff rod which is mounted to the surface of the sheet metal. It is called a ‘fixed-mast antenna’ in contrast to a power antenna. It is usually mounted in one of three basic locations: on either side of the front fender ahead of the A-pillar; either side of the rear fender behind the backlight (i.e., rear window); on the front or back of the roof. Fixed-masts are relatively trouble-free, unlike power antennas which rely upon a motor that may fail. However, some fixed-masts are subject to breakage by vandals or car-washes.
- Fixed orifice tube
- A device that converts high pressure liquid refrigerant into low pressure liquid refrigerant (thus lowering its boiling point) before it passes through the evaporator. The expansion valve replaces the thermostatic expansion valve. Also called an Expansion tube
- Fixed price selling
- Published fixed price displayed on a new vehicle eliminating need for negotiation.
- Fixed stop
- A Stop that cannot be changed without the use of special tools.
- Fixed Tandem
- Assembly of two axles and suspension that is attached to the chassis in one place, and cannot be moved fore and aft.
See
- Fixed wheel
- Same as Fixed gear, the kind of rear wheel found on track bicycles.
- Fixed wheel bicycle
- A bicycle you can back-pedal to brake. It has one wheel which cannot rotate independently of the pedals
- Fixte
- A bicycle with a single rear gear that does not allow for coasting. In other words, you have to pedal all the time.
- Fixture
- Device for holding goods in process while working tools are in operation that does not contain any special arrangements for guiding the working tools.
- Flag
- The triangular area of a car’s front door, just above the beltline and behind the A-pillar, to which the outside rearview mirror is often attached. The flag also shortens the front-door glass, allowing it to lower completely into the door.
- Flag down
- The action of a pedestrian to stop a vehicle by using a hand signals (usually waving the arms laterally above the head). This is usually a sign of an emergency
- Flagger
- A worker who has completed flagging certification training, has a current certification, and is employed to provide traffic control services within the work zone.
- Flagship model
- The prestige model or top model of a manufacturer’s line of vehicles, e.g., ‘Cadillac is the flagship model for GM and Lincoln is the flagship model for Ford.’
- Flags of convenience
- Flags of nations which offer favorable tax structures and regulations. Ships registering under the laws of these nations are not always required to establish their home location in that country.
- Flagstaff
-
- Flagpole at stern of ship; ensign staff.
- Flagpole attached to bicycles and mobility scooters
- Flame arrester
- A device installed in the air filter housing which prevents flames from escaping into the engine compartment during a backfire.
- Flame front
- The term used to describe certain aspects of the fuel explosion in the cylinders. The flame front should move in a controlled pattern across the cylinder, rather than simply exploding immediately.
See
- Flame glow plug
- A glow plug that preheats the intake air by burning a small quantity of precisely metered fuel
- Flame Hardening
- A process of case hardening
- Flame paint
-
1933 Ford with flame paint
A popular (during the 1950s) special paint design applied to the front of custom cars. Large flames in yellow, orange, and red were painted on the side of the car from the back of the front wheels toward the back
- Flame test for leaks
- Tool which is principally a torch. When a halogen mixture is fed to the flame, this flame will change color in the presence of heated copper.
- Flame trap
- A device consisting of a valve or similar, preventing the escape of ignited Blow back gases, usually located in the hose or pipe leading from the crankcase to the intake tract
- Flammable Liquid
- Flammable liquids are Class I liquids. A liquid having a flash point below 37.8°C and having a vapor pressure not exceeding 276 kPal at 37.8°C. Class I liquids are subdivided as follows:
- Class IA — Includes those having flash points below 22.8° and having a boiling point below 37.8°C.
- Class IB — Includes those having flash points below 22.8° and having a boiling point at or above 37.8°C.
- Class IC — Includes those having flash points at or above 22.8° and below 37.8°C.
- Flange
-
- A projecting rim or collar on an object for keeping it in place. It adds strength or provides a means of attaching another part.
- The parts of a hub shell to which spokes are attached and which secure the tire on the rim base.
- The circle of metal inside the teeth on a chainring.
- Right angle bends in sheet metal designed to give rigidity or to eliminate a sharp edge. Commonly called bends.
- A part of a plate or shape at, or nearly at, right angles to main part; to bend over to form an angle.
- Flange bolt
- A bolt with a fillet as part of the bolt head

- Flanged head
- A bolt head which has a fillet (i.e., it looks as though it already has a washer under the head; but the washer is part of the head)
- Flange height
- A measurement from the top of the flange to the Bead seat, and is the difference between the overall diameter and Nominal rim diameter, divided by two.
- Flange joint
- A coupling between two shafts formed of two disc-shaped flanges on the ends of the shafts which are bolted to each other
- Flange mount carburetor
- A carburetor mounted by a flange bolted to a manifold on the cylinder or cylinder head. An insulator block and gasket are used to seal and insulate the carburetor.
- Flange seal
- An L-shaped rubber seal used in some earthmover tubeless tire mountings. It prevents air loss between the tire beads and both the flange and rim base, and the flange and loose taper seat.
- Flank
-
- The side of a screw thread, rising from the bottom of the groove to the top of the ridge
- One of the two flat parts of the face of a cam
- Flap
-
- A rubber protector used in tube-type truck tires to prevent injury to the tube by the bead toes and at the valve slot of the rim.
- A flat piece of material attached along one side, often by a hinge and forming a small door for shutting off an opening.
- Flapper valve
- Thin metal valve used in refrigeration compressors which allows gaseous refrigerants to flow in only one direction.
- Flare
-
- A flange or a cone-shaped end applied to a piece of tubing to provide a means of sealing two similarly angled areas formed in fitting the body and the nut.
- A sudden burst of flame.
- The spreading out of the hull form from the central vertical plans, usually in the front, much like the end of a trumpet.
- A gradual spreading or widening of a tube.
- An enlargement at the end of a piece of flexible tubing by which the tubing is connected to a fitting or another piece of tubing. This enlargement is made at about a 45 deg. angle. Fittings grip it firmly to make the joint leakproof and strong.
- The sudden widening of the shell at top near the bow.
- Flared
- Gas disposed of by burning in flares usually at the production sites or at gas processing plants.
- Flared wheel arch
- A wheel arch bent outwards around its circumference, usually to accommodate wider wheels and/or tires
- Flare nut
- A nut fitting over the flared end of a brake or fuel pipe at a union and used to clamp the tubing flare against another fitting.
- Flare nut spanner
- British term for Flare nut wrench
- Flare nut wrench
-
Flare nut wrench
- A wrench which looks almost like an open end wrench except the end curls around the nut farther. The opening allows the wrench to slide over a tube or pipe to which a nut is attached, but not directly over the nut. Thus you have to slide it over the pipe first and then bring it up to the nut. The wrench has more faces than an open end wrench thus giving better gripping.
- A wrench designed for loosening hydraulic fitting tube nuts (flare-nuts) without damaging them. Flare-nut wrenches are kind of like a six-point box-end wrench with one of the flats missing, which allows the wrench to pass over the tubing but still maintain a maximum amount of contact with the nut
- Flareside Truck
-
Flareside Truck
Ford’s term for a pickup truck style in which there is some kind of indentation just behind the cab to allow you to enter the bed in contrast to a Styleside truck. Chevrolet calls this style Stepside
- Flaring tool
-
Flaring tool
A tool used to form Flare connections on tubing.
- Flash
-
- The first stage of the drying process of paint where most of the Solvents evaporates.
- A sudden burst of energy.
- When crude oil is heated the lighter or more volatile vapor is separated and travels to the top of the tank. This traveling is called flash.
- The impact of electric arc rays against the human eye.
- The fin of surplus metal formed at the seam of a resistance weld.
- To use your signal lights as in ‘My car was flashing left.’
- To rapidly switch the headlights off and on — usually to indicate a warning. If you are behind someone and you flash your headlights, it means that you want him to pull over so you can pass. If you see someone flashing his lights, it could mean that there is a police car ahead so slow down; or it could mean there is danger ahead (e.g., deer on the road, an accident ahead, etc.). In some places, flashing your lights is illegal.
- Flashback
- Another term for Blow back
- Flasher
-
- A flashing signal light.
- An electronic switch apparatus controlling the operation of the signal lights, including their rate of flash; self-cancelling when the steering wheel is returned to the straight-ahead position.
- An electronic relay which regulates the signal lights and emits a clicking or chiming sound.
- Flash gas
- Instantaneous evaporation of some liquid refrigerant in evaporator which cools remaining liquid refrigerant to desired evaporation temperature.
- Flashover
- Tendency of electrical current to travel down the outside of a spark plug instead of through the center electrode. It usually occurs when the sparkplug is dirty or oily since electricity finds that to be the path of least resistance.
- Flash point
-
- The point in the temperature range at which a given oil (especially diesel oil) in vapor form will ignite and flash into flame. The higher the flash point, the better the lubricating quality of the oil. The temperature at which the vapor continues to burn is called the fire point.
- Temperature at which flammable liquid will give off sufficient vapor to support a flash flame but will not support continuous combustion.
- The minimum temperature at which the liquid gives off vapor in sufficient concentration to form an ignitable mixture with air near the surface of the liquid within the vessel as specified by appropriate test procedure and apparatus as follows:
- The flash point of a liquid having a viscosity less than 45 SUS at 37.8°C and a flash point below 93.4°C is determined in accordance with the Standard Method of Test for Flash Point.
- The flash point of a liquid having a viscosity of 45 SUS or more at 37.8°C or a flash point of 93.4°C or higher is to be determined in accordance with the Standard Method of Test for Flash Point.
- Flash time
- The time required for a Coat of paint to lose most of its Solvent through Evaporation.
- Flash weld
- Resistance type weld in which mating parts are brought together under considerable pressure while a heavy electrical current is passed through the joint to be welded.
- Flat
-
- When a battery has completely discharged, so that it cannot turn over the engine then the battery is said to be flat.
- To be completely deflated, especially as the result of a puncture or a leaky valve.
- A deflated tire.
- To experience a flat tire as in ‘While riding my bike, I flatted.’
- An engine having horizontally opposed cylinders.
- A level area on an otherwise rounded surface.
- To give a final light rubbing down to (paintwork or filler) with fine grade sandpaper or similar, to prepare the surface for a top coat.
- A small partial deck (built level) without curvature.
- Flat base rim
- A truck rim with no center depression. A demountable flange (consisting of 1 or 2 piece side/lock ring) permits the removal of the tire and holds it in place after installation.
- Flat base rim taper
- An obsolete form of rim with no taper at either Bead seat.
- Flat battery
- A British term for a Dead battery
- Flatbed trailer
-
Flatbed trailer
A trailer with a flat deck (and no sides or top) so that any size or shape item can be loaded (within reason) regardless of height, length, or width
- Flatbed truck
-
Flatbed truck
A truck with a flat deck (and no sides or top) so that any size or shape item can be loaded (within reason) regardless of height, length, or width
- Flat-bladed screwdriver
- A screwdriver which has a blade at its end to fit slotted screws. This type is the least desirable screw giving the least amount of torquing ability. If the screwdriver does not fit well, the screw is easily damaged.
- Flat crank
- A crankshaft having one of the bearing Journals out-of-round.
- Flat cylinders
- Found in the flat-four- and flat-six-cylinder engines used in Honda’s Gold Wings, the cylinders are arranged in a flat, opposing configuration
- Flat eight
- An eight cylinder engine with four cylinders on each side. The ‘left’ bank of four cylinders is directly opposite the right bank.
- Flat engine
-
Flat engine
An engine where opposite cylinders are 180 degrees apart. This engine type is found on the VW Beetle, Corvair, Porsche six-cylinder, Subaru quadrazontal, and BMW motorcycle engines.
- Flat-faced
- A colloquial term for a Cab-Over-Engine truck
- Flat file
- A long, thin rectangular bar (like a blade) with angled grooves cut into the top and bottom of the larger sides and used to shape metal
- Flat four
-
Flat four
A four cylinder engine with two cylinders on each side. The left bank of two cylinders is directly opposite the right bank.
- Flat Front Bus Type
- The shape of typical transit and shuttle buses. Flat-nosed buses, can either be front, mid-ship or rear engine. Most non-articulated transit versions are rear engine; articulated versions may have the engine in the rear of the second unit (true pushers) or mid-ship, at the rear of the first unit. Can be low floor configuration (level floor area to front of vehicle fairly even with curb height) or standard platform (about 2-3 steps from curb to passenger platform. Some transit buses have a kneeling feature, fold-out ramps, or even may be equipped with a lift to accommodate special needs passengers. No cargo capacity under floor.
- Flathead
-
Flathead
An engine with all the valves in the block on one side of the cylinder. Also called L-head because the cylinder acts as one side of an inverted L while the valves act as the other side. Since there are no valve in the head, the head can be flat.
- Flathead machine screw
-
Flathead machine screw
A machine screw with a flat top and a conical bearing surface designed for a countersunk hole and to fit flush with the surface of the plate it joins.
- Flat hump
- A raised and flattened portion on the Bead seat of some wheel rims which retains the beads of an insufficiently inflated tire on the bead seat, thereby preventing the tire beads from jumping into the rim well.
- Flat Keel
- The bottom shell strake on centerline of ship.
- Flatnose
- See Bullnose.
- Flat-nose pliers
- A common pair of pliers where the ends of the jaws do not extend to a point (like Long-nose pliers); but are cut short. Also called flat-nosed pliers.
- Flat-nosed pliers
-
Flat-nosed pliers
A common pair of pliers where the ends of the jaws do not extend to a point (like Long-nose pliers); but are cut short. Also called flat-nose pliers.
- Flat pente
- A raised portion on the Bead seat of some wheel rims which retains the tire beads of an insufficiently inflated tire on the bead seat, thereby preventing the beads from jumping into the rim well. This is a compromise between the Contre pente and the Flat hump contours and is mainly used on passenger cars made in France.
- Flat plate keel
- The horizontal, centerline, bottom shell strake constituting the lower flange of the keel
- Flat plate pumped
- A medium-temperature solar thermal collector that typically consists of a metal frame, glazing, absorbers (usually metal), and insulation and that uses a pumped liquid as the heat-transfer medium: predominant use is in water-heating applications.
- Flat point socket set screw
- A headless socket set screw threaded the entire length. It has a hexagonal drive at one end and a flat surface at the other end.
- Flat position welding
- Creating a horizontal weld on the upper side of a horizontal surface. Also called downhand welding
- Flat rate
- A pre-determined length of time set down by the manufacturer that a particular repair job will take and is listed in the Flat rate manual. If the flat rate is two hours, but the mechanic completes the job in more or less time, you will be charged for two hours. For the shop, flat rate encourages mechanics to work harder to beat the prescribed time, thus earning more for the shop and the mechanic; but it also hurts the shop when the mechanic cannot complete the job because of other contributing factors (i.e., a bolt which should have taken 10 seconds to remove breaks off and requires 30 minutes to remove). For the customer, flat rate means fair pricing for the same job no matter how long it actually took. Thus both Sam’s labor bill and my labor bill to do the same work is the same cost. It can be unfair if the mechanic worked faster on my vehicle (because I keep it in excellent shape) than on Sam’s vehicle (because his involved a lot more cleaning, etc. to do the job). Also, there is the danger that a mechanic may take shortcuts in order to beat the flat rate, but which may cause mechanical problems later. Charging by the actual time the mechanic takes is called Straight time.
- Flat rate manual
- A listing of almost every job that can be done on a vehicle with the time required for a mechanic to do the work. It is used in service shops to determine labor charges. If a mechanic completes the job before the Flat rate time, the Customer is still charged the flat rate time. If he exceeds the flat rate time, the Customer is not charged for Straight time, but the lower flat rate time.
- Flat six
- A six cylinder engine with three cylinders on each side. The left bank of three cylinders is directly opposite the right bank.
- Flat Socket Head Cap Screw
-
Flat Socket Head Cap Screw
Similar in design to a button socket head cap screw but with an 82° countersunk flat head. Used when a flush mounting, high strength screw is required. Commonly used in tools and dies where moving parts pass over the fastened area.
- Flat spot
-
- Refers to a spot during an acceleration period where the engine seems to lose power for a moment and will then begin to pull again.
- Irregular wear in an isolated spot or spots around the tire tread. It is usually caused by locking the brakes so that the tire skids on the ground.
- Flat spring
- A long bar that is bent in the middle. When pressure is applied to the outside ends, the middle flexes.
- Flat tire
- A condition where an air-inflated tire is no longer pressured up with air. The problem may be a cut in the casing or tube; or may be caused by a bad valve. When you experience a flat tire, no doubt some wit will tell you that your tire is flat only on the bottom.
- Flat twin
- A two cylinder engine with one cylinder on each side. The left cylinder is directly opposite the right cylinder.
- Flèche vélocio
- A 24-hour team bicycle ride covering at least 360 kilometres held over the Easter weekend in France.
- Fleet car
- A company will purchase a number of cars at a low price, often basic models, from one manufacturer. When the company decides to sell these cars, it will advertise that they were fleet car. Fleet cars have the advantage of regular maintenance; but the disadvantage of high mileage.
- Fleetside
-
Fleetside
Chevrolet’s term for a bed design in contrast to the Stepside in that there is no indentation behind the cab
- Fleet vehicle
- Any motor vehicle a company owns or leases that is in the normal operations of a company. Vehicles which are used in the normal operation of a company, but are owned by company employees are not fleet vehicles. If a company provides services in addition to providing natural gas, only those vehicles that are used by the natural gas provider portion of a company should be counted as fleet vehicles. Vehicles that are considered off-road (e.g., farm or construction vehicles) or demonstration vehicles are not to be counted as fleet vehicles. Fleet vehicles include gasoline/diesel powered vehicles and alternative-fuel vehicles.
-
A model of automobile manufactured by the Cadillac division of General Motors from 1927-96
- Flex arm suspension
- Rear axle design with torsionally flexible axle beam in line with the rear wheels and trailing links
- Flex disc
-
Flex disc
Similar to Flexible coupling, but the term Flex Disc is used in Mercedes documentation to specify the flexible coupling at both ends of the driveshaft.
- Flexibility
-
- Elasticity of a material.
- The ability of an engine to go down to low speeds in a high gear and pull away smoothly without gearing down, which is governed mainly by its torque characteristics
- Flexible
-
- The ability to bend without breaking.
- The ability of an engine to go down to low speeds in a high gear and pull away smoothly
- Flexible brake pipe
- A pipe connecting the wheel cylinder to the rest of the system, which has to flex to allow for the up and down movement of the wheel
- Flexible coupling
- A simple shaft coupling used where only small angles of misalignment between the two shafts occur, as in a steering column, the drive being transmitted either by tension-stressed fabric discs or pressurized rubber blocks
- Flexible drive
- A drive consisting of a cable in an outer sheath, used for mainly light applications such as speedometers, rev counters and windshield wipers
- Flexible drive handle
- A socket drive tool with a pivoting head for use with sockets, its length gives good leverage and access to difficult locations because of its ability to bend
- Flexible fuel vehicle
- A vehicle that can operate on
- alternative fuels (such as M85 or E85)
- 100-percent petroleum-based fuels
- any mixture of an alternative fuel (or fuels) and a petroleum-based fuel.
Flexible fuel vehicles have a single fuel system to handle alternative and petroleum-based fuels. Flexible fuel vehicle and variable fuel vehicle are synonymous terms.
- Flexicoking
- A thermal cracking process which converts heavy hydrocarbons such as crude oil, tar sands bitumen, and distillation residues into light hydrocarbons. Feedstocks can be any pumpable hydrocarbons including those containing high concentrations of sulfur and metals.
- Flex-LocTM
-
Flex-LocTM
A locking nut with a series of slots. The locking threads of the slotted top press inward against the bolt, lifting the nut upward and causing the remaining threads to bear against the lower surface of the bolt threads.
- Flickability
- The ease with which the bike can be leaned to the right or left around turns. High flickability means it leans quickly and easily, acting like a sportbike. Low flickability is how a cruiser handles — not really designed for fast riding through the canyons. Lighter, smaller bikes are generally more flickable through turns.
- Float
-
- A small hollow tank which is more buoyant than the liquid in which it is immersed. In a carburetor it operates the valve (Needle and seat) which controls the amount of fuel entering the carburetor. In the fuel tank, it indicates the amount of fuel. Older floats were hollow and made of metal, but newer ones are made of a solid synthetic material.
- The action of the Breaker arm when it is pushed out as the cam strikes the rubbing block; and before the arm can return after the cam has passed, the next cam strikes the block and re-opens it. In other words, the breaker arm never has the time to fully close before being opened again.
- The action of a component to move freely because it is not firmly attached.
- Float assembly
- A plastic or hollow brass device attached to an arm that pivots on a pin and raises and lowers, opening and closing the float needle to control the fuel level in the carburetor.
- Floatation
- The ability to float generally referring to large low pressure tires (i.e., the ability of a tire, to pass over soft surfaces without sinking in.)
- Float bowl
- That part of a carburetor that acts as a reservoir for gasoline and in which the float is placed. The float controls the amount of fuel moving through the fuel valve.
- Float bumper spring
- A small spring installed under the float tang to minimize float bounce and vibration
- Float chamber
- British term for float bowl
- Float circuit
- The portion of the carburetor (float, needle, seat) devoted to maintaining a constant float level.
- Float height
- A measurement of the carburetor float. With the carburetor upside down and the float hanging freely, it is the distance from the gasket surface of the float bowl to the edge of the float. Usually a manufacturer’s specification for calibrating the float level.
- Floating caliper
-
- A single piston caliper which moves (floats) when the brakes are applied.
- In a hydraulic disc brake system, the assembly connected to a movable arm and holds one piston and both inside and outside brake pads to press against a brake disc.
- Floating caliper disc brake
- A disc brake with a single piston, in which the caliper itself can move to bring both pads into contact with the disc
- Floating cam
- Brake cam or other type of expander which is not rigidly mounted in the brake backplate of a drum brake, so that it can exert equal pressure on the two shoes
- Floating cup
- The type of accelerator pump inlet valve used on all current Rochester Quadrajet carburetors. It fills the accelerator pump well through the center of the pump piston cup. Designed to fit on the plunger with a small amount of vertical clearance. During delivery stroke, the cup is forced up against piston face, sealing off a fill hole in the face. As plunger and piston travel upward on return stroke, the cup drops a few thousandths of an inch from piston face and fuel enters through hole in the face.
- Floating frame
- A frame which holds the cylinder assembly and is supported by the mounting frame, usually made of heavy-gauge sheet steel.
- Floating piston pin
- A Piston pin which is not locked in the Connecting rod or the piston, but is free to turn or Oscillate in both the Connecting rod and the piston.
- Float level
-
- Height of the fuel in the carburetor float bowl. Controlled by the float, needle, and seat.
- The specific float setting that will produce the correct fuel level.
- The float position at which the float needle closes against its seat, shutting off the fuel inlet valve to prevent further deliver of fuel
- Float needle
- A needle in the carburetor which is activated by the level of fuel in the float bowl. As the level drops, the needle lifts and allows more fuel to enter the bowl
- Float valve
- Type of valve which is operated by sphere or pan which floats on liquid surface and controls level of liquid.
- Flood
-
- To allow too much fuel to enter the carburetor or the engine.
- A condition where the fuel mixture is overly rich or an excessive amount has reached the cylinders. Starting will be difficult and sometimes impossible until the condition is corrected.
- Floodable length
- The length of ship which may be flooded without sinking below her safety or margin line. The floodable length of a vessel varies from point to point throughout her length and is usually greatest amidships
- Flooded engine
- An engine which has too much fuel into the cylinders. It can be caused from trying to repeatedly start a car which refuses to start. If this condition continues, the engine oil could become diluted and should be changed.
- Flooded evaporator
- Evaporator containing liquid refrigerant at all times.
- Flooded system
- Type of refrigerating system in which liquid refrigerant fills most of the evaporator.
- Flooded system, high-side float
- Refrigeration system which has a float operated by the level of the high-side liquid refrigerant.
- Flooded system, low-side float
- Refrigerating system which has a low-side float refrigerant control.
- Flooding
-
- A condition where the fuel mixture is overly rich or an excessive amount has reached the cylinders. Starting will be difficult and sometimes impossible until the condition is corrected.
- Act of allowing a liquid to flow into a part of a system.
- A term which refers to overcharging the system
- Flood the carburetor
-
- An undesirable condition which occurs when the float in the carburetor is set too high.
- A desired condition which allows extra fuel into older or simpler carburetors by pushing down the float with an extra lever (called a tickler) to give a richer mixture for starting
- Floor
-
- The flat base panel of a vehicle.
- A verb meaning to push the accelerator as far as it will go (i.e., to the floor).
- The vertical transverse plate immediately above the bottom shell plating, often located at every frame, extending from bilge to bilge.
- Floorboard
- The flat base panel of a vehicle. Originally it was the collection of wood planks which made up the floor of vehicle. The floor of the vehicle under the Instrument panel.
- Floor change
-
- A gear shifter on the floor — usually on the center console.
- Some coins left on the floor after being negligently dropped there.
- Floor Freight
- Heavy freight that must be loaded on the trailer floor and not on top of light or delicate freight.
- Floor jack
-
Floor jack
A device for lifting the vehicle, or part of the vehicle, off the ground to facilitate repairs. It has wheels to allow it to move to the best location and is activated by hydraulic pressure as the long arms are inserted and pumped up and down.
- Floor Load
- Refers to product stacked directly onto the floor of a trailer without pallets or slip sheets; product must be unloaded manually without the use of a forklift.
- Floormat
-
- The factory installed carpet applied to the cabin floor of a vehicle.
- The removable piece of carpet used to protect the factory installed carpet.
- Floor pan
-
- The metal structure on the bottom of the car. Almost all newer cars are unit body (or unibody) construction, and the floor pan provides the foundation for chassis stiffness. Your feet usually rest on a floor pan when you are in a car.
- The large stamped metal part of the car’s body over which the carpet is laid. Usually assembled from several smaller stampings, the floorpan forms the floor and fixes the dimensions for most of the car’s external and structural panels. It is also the foundation for many of the car’s mechanical parts.
- Floorpan
-
See
- Floor shift
- When the shifting lever is placed in a vehicle, it usually occupies one of three primary positions the dash (usually a Pushbutton arrangement); the Steering column; and on the center column between the driver and front seat passenger.
See
- Flotation
- Characteristic of a vehicle, by reason of large softly inflated tires, not to sink on soft going such as mud, sand, or snow.
- Flow check piston
- Piston assembly, with an orifice in the center, which can operate as an expansion valve.
- Flow control
- The regulation of the amount of fluid passing through a pump, especially important under changing operating conditions
- Flow detachment
- The deviation of the gas flow into the cylinder from its ideal path, thus losing its stability, caused by swirl and/or improper combustion chamber design etc.
- Flowmeter
- A meter indicating the amount of liquid passing through, used for instance to supply information to a fuel consumption indicator.
- Flow Rack
- Racking equipment that allows for the product to be stocked in through one side and removed for order fulfillment purposes from the other side. Product stored in Flow Rack is naturally allocated via FIFO based on the racking equipment design.
- Flow-Through Distribution
- A process in which goods from multiple locations are brought into a central point, resorted by delivery destination and shipped in the same day. Typically involving a combination of truckload and less-than-truckload carrier resources, this practice eliminates warehousing, reduces inventory levels and speeds order turnaround time.
- Flow-through ventilation
- A system which allows (or even forces) outside air into the passenger compartment through the dash and leaves through openings in one of the pillars (usually the C-post) or rear quarter panels.
- Flue
- A gas or air passage which usually depends on natural convection to cause the combustion gases to flow through it. Forced convection may sometimes be used.
- Flue gas
- A product of combustion plus excess air in the Appliance flue or heat exchanger.
- Flue gas baffle
- An object in the path of the flue gases and exposed to flue gases or radiant heat, which is intended to restrict or modify flue gas flow. It may be a projection from the heat exchanger or suspended in the flue gas passages by some other means.
- Flue gas desulfurization
- The action of removing sulfur oxides from the combustion gases of a boiler plant before discharging to the atmosphere. Also referred to as scrubbing. Chemicals such as lime are used as scrubbing media.
- Flue-gas desulfurization unit
- Equipment used to remove sulfur oxides from the combustion gases of a boiler plant before discharge to the atmosphere. Chemicals such as lime are used as the scrubbing media. Also called a scrubber.
- Flue-gas particulate collector
- Equipment used to remove fly ash from the combustion gases of a boiler plant before discharge to the atmosphere. Particulate collectors include electrostatic precipitators, mechanical collectors (cyclones), fabric filters (baghouses), and wet scrubbers.
- Fluid
-
- A substance which flows, e.g., a liquid or a gas.
- Substance in either a liquid or gaseous state; substance containing particles which move and change position without separation of the mass.
- Any liquid or gas that is capable of flowing and that changes its shape at a steady rate when acted upon by a force tending to change it shape. A term used to refer to any substance having the above properties.
- Fluid capacities
- The full amount of oil in the crankcase; water in the radiator and cooling system; or fuel in the gas tank; washer fluid in the reservoir tank; etc.
- Fluid catalytic cracking
- The refining process of breaking down the larger, heavier, and more complex hydrocarbon molecules into simpler and lighter molecules. Catalytic cracking is accomplished by the use of a catalytic agent and is an effective process for increasing the yield of gasoline from crude oil. Catalytic cracking processes fresh feeds and recycled feeds.
- Fluid clutch
- A hydraulically acting coupling by which power can be transmitted, used as an automatic clutch with a driving and a driven rotor revolving in oil which acts as the transmission medium
- Fluid coking
- A thermal cracking process using the fluidized-solids technique to remove carbon (coke) for continuous conversion of heavy, low-grade oils into lighter products.
- Fluid coupling
-
Fluid coupling
On a manual transmission, there is a mechanical connection between the engine and transmission through the clutch. On an automatic transmission a fluid coupling provides a Viscous fluid to connect the engine output and the transmission. It transfers engine torque to the transmission Input shaft through the use of two units with Vanes (called a Torus) operating very close together in a bath of oil. The engine drives one torus causing it to throw oil outward and into the other torus which then begins to turn the transmission Input shaft. A fluid coupling cannot increase torque above that produced by the crankshaft. Buick’s Dynaflow is an example of this kind of coupling.
- Fluid flywheel
- A kind of fluid coupling in which the flywheel is the driving rotor
- Fluid level warning indicator
- A warning light on the instrument panel which is illuminated when the level of fluid in the a system is too low
- Fluid pressure gauge
- An instrument for measuring fluid pressure in a system, such as oil pressure or fuel pressure.
- Fluorescent lamp
- A glass enclosure in which light is produced when electricity is passed through mercury vapor inside the enclosure. The electricity creates a radiation discharge that strikes a coating on the inside surface of the enclosure, causing the coating to glow.
- Fluorescent screen
- A glass coated with a lumininescent substance that will ‘glow’ when excited as found in cathode-ray tubes
- Fluorocarbon
- Any of a class of compounds produced by substituting fluorine for hydrogen in a hydro-carbon and characterized by great chemical stability. Fluorocarbons have numerous industrial applications, such as dichlorodifluoromethane or R-12
- Flush
-
- To cleanse a system by sending water or other liquid through a system.
- To align two items so that they fit evenly or level.
- Operation to remove any material or fluids from refrigeration system parts by purging them to the atmosphere using refrigerant or other fluids.
- The removal of solid particles and sludge such as metal flakes or casting flash, dirt or oil by running a pressurized cleaning solution through components and refrigerant lines
See
- Flush deck ship
- A ship constructed with upper deck extending throughout her entire length without a break or a superstructure, such as forecastle, bridge or poop
- Flushing
-
- To cleanse a system by sending water or other liquid through a system.
- Removing old brake fluid from a hydraulic brake system by pumping new brake fluid through the system.
- Flushing tee
- A device with three hose necks laid out in the shape of the letter T that is spliced into a heater hose, secured with hose clamps. the neck on the stem is covered with a threaded cap, which is removed and a household water hose is attached (with a special adapter) to run water though the cooling system to flush out dirt, rust, etc. from the engine.
- Flushing the cooling system
- The process of circulating water through the cooling system to remove old coolant along with any dirt or rust. Back flushing means circulating the water from the engine to the radiator (reversing the normal direction of flow) in order to clean the system more efficiently.
See
- Flush mounted speaker
- A radio or stereo speaker mounted in a cutout in the interior trim so that it does not project out. The opposite of surmounted speakers.
- Flush Pallet
- A pallet with deck boards flush with the stringers, stringer-boards or blocks along the sides of the pallet.
- Flute
- A groove in a cutting tool that forms a passageway for the exit of chips removed during the cutting process.
- Flux
-
- The lines of magnetic force moving through a magnetic field.
- the magnetic field that is established around an energized conductor or permanent magnet
- An ingredient placed on metal being Soldered or Brazed, to remove and prevent the formation of surface oxidization which would make soldering or Brazing difficult. Flux promotes the fusion of metals during the welding process.
- Flyweights
- Special weights which react to Centrifugal force to provide automatic control of other mechanisms such as accelerators or valves.
- Flywheel
-
Flywheel
A relatively large and heavy metal wheel that is attached to the back of the crankshaft to smooth out the firing impulses. It provides inertia to keep the crankshaft turning smoothly during the periods when no power is being applied. It also forms a base for the starter ring gear and, in vehicles with manual transmission, for the clutch assembly.
- Flywheel generator
- A small alternator of the rotating magnet type attached to one end of the crankshaft and spinning with it, acting as an additional flywheel; now used only in mopeds or scooters
- Flywheel magneto ignition system
- An ac ignition system using a generating coil and either a magnetic trigger (CDI) or contact points as well as a flywheel to provide secondary current.
- Flywheel puller
- A specially designed tool with three arms and a center stud used to removing the flywheel. The three arms are attached to three mounting points (either on the rim of the flywheel or into three threaded holes in the flywheel). The center stud is screwed into the center of the flywheel and pushes against the end of the crankshaft. As the stud pushes in, the flywheel is forced away from the crankshaft.
- Flywheel ring gear
- A gear on the outer circumference of the Flywheel. The Starter drive gear engages the Ring gear and Cranks the engine.
- Flywheel turner
- A special tool used for hand cranking the engine while working on clutches, gearboxes, etc. or doing jobs that require that the crankshaft be in a specific position. It consists of a handle and lever to hook into the starter ring teeth
- FM
-
- Abbreviation for Frequency modulation. A term used to describe a type of radio frequency in which the frequency of the wave changes rather than the amplitude.
- Abbreviation for Fan Motor Program in PCM
See
- FMVSS
- Abbreviation for Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standards and Regulations, a division of the U.S. Department of Transportation. Similar to the CMVSS
FNA
vehicle brand of which the 1925-1948 models with required application are classic cars.
- Foam
- Foaming
-
- The formation of bubbles in the oil of a transmission, differential, or shock absorber, etc.
- The formation of bubbles in the oil and refrigerant caused by a rapid boiling out or evaporation of the refrigerant dissolved in the oil when the pressure is suddenly reduced. This is most likely to occur when the compressor starts and the pressure is suddenly reduced. If noted in the sight glass, this condition indicates a very low refrigerant level.
- Undesirable characteristic of oil being whipped into a froth (air and oil solution).
- Foam leak detector
- System of soap bubbles or special foaming liquids brushed over joints and connections to locate leaks.
- FOB
-
- Abbreviation for Freight on Board or Free on Board Used to describe when goods are loaded for free on a delivery vehicle at the seller’s place of business, but the buyer has to pay transportation charges to the delivery destination.
-
Key fob
When not an abbreviation, it refers to the device on a key chain which may contain your name or a company name, etc. Sometimes called a key fob.
- FOB Vessel
- Title/transportation costs transfer after goods are delivered on vessel. All export taxes/costs involved in overseas shipments are assessed to the buyer.
- Fog coat
-
- A fully reduced (thinned) paint that is sprayed at higher than normal air pressure or with the gun held at a greater distance than normal from the work. The object is to obtain a fast Flash-off (Evaporation) of Thinner with minimum penetration of Thinner into the old paint.
- Light finish oil spray applied over seal coats to keep chips in place. Normally used in high traffic/speed areas.
- Fog light
-
Fog light
- A light (usually in pairs) mounted at the front of a vehicle which is designed to give a wide low beam which penetrates fog and rain, etc. and illuminates the sides of the road.
- A red light mounted at the back of a vehicle which has the same intensity as a brake light to help following vehicles to see your vehicle.
See

- Foil
- A light, thin, blunt-edged sword from which an Air foil is named.
- Folding camping trailer
-
Folding camping trailer
A lightweight recreational unit used for camping. Sometimes called tent trailer or pop-up trailer. The ends fold out and the top is raised to reveal a camping unit. When being pulled, the ends fold down to make a compact unit. The lightweight allows it to be towed by most cars. The trailer can be unhitched from the car for easier parking or for leaving it at the campground while you go to town for supplies. The interior contains kitchen, dining room, and sleeping facilities. Usually there is a pair of double beds and the dining bench converts into a bed. Often there is a cooking stove, sink, heater, refrigerator, a fresh water tank, a waste water tank, a faucet, a sink, a LP (propane) gas supply, and a separate 100-125 volt electrical system. They can sleep up to six people. Prices begin at around $4,000 and can go as high as $25,000.
- Folding rear seats
- Rear seats in a hatchback, station wagon, or van which fold forward into the footwells to give a more or less flat loading area.
- Fold-ups
-
Greenspan GT3
A three-wheel tadpole cycle that folds along the center boom to a more compact size for transporting. Example: Greenspeed GT3
- Follow-up spark
- Secondary spark occurring when a spark is extinguished and re-ignited in the course of the spark duration, especially if the mixture is turbulent
- Follow-up-type valve
- A unit which responds to fluid displacement or mechanical linkage movement, to modulate pressure in a cylinder or chamber.
- FOM
- Abbreviation for fix operating mode a Limp-home mode
- Fome-Cor®
- A trade name for a material used in the designing of interior bucks and mockups. Fome-Cor typically consists of a 1/8 to _ inch sheet of Styrofoam sandwiched between two layers of heavy, white paper.
- Foot pedal
- One of four possible pedal located on the floor in front of the driver gas pedal (accelerator), brake pedal, Clutch pedal, or Emergency brake pedal
- Footpedal cluster
- The gas and brake pedals in a vehicle with automatic transmission and the gas, brake, and Clutch pedals in a manual transmission vehicle.
- Footpeg
- The metal post (usually covered in rubber) found on either side of a motorcycle upon which the rider or his passenger places his feet.
- Footplate
- A platform upon which your foot rests. It is distinguished from a pedal. A footplate allows you to rest your foot, but no action takes place. However, when you place your foot on a pedal some action could take place.
- Foot pound
- Unit of work. A foot pound is the amount of work done in lifting one pound one foot. Usually spelled with a hyphen.
- Foot-pound
- (ft-lb) A measurement of the work involved in lifting one pound one foot. In tightening, it is one pound pull one foot from the center of an object. torque, or the twisting motion of an engine, is expressed in terms of foot-pounds at a specified rpm.
- Footwell
- A recess in the floor below the feet of the rear seat occupants, but may also be used for the space used by the feet of people in the front seats
- Footwell intrusion
- A situation where an engine, for instance, occupies some of the space normally allocated for the feet of the driver and his passengers.
- Force
-
- A push or a pull that causes objects to change their motion.
- That influence on a body which causes it to accelerate.
- It is a Vector quantity, with a particular direction and forces must be combined with special Vector rules.
- In the SI (international system of units), it is measured in newtons (N); but the older measurement recorded force in pounds, ounces, and feet.
- Accumulated pressure. If the pressure is 10 psi on a plate 10 in. sq., the force is 100 lb. If pressure is 10 kg/cm² on a plate 10 cm² in area, the force is 100 kg.
- Forced convection
-
- Transfer of heat resulting from forced movement of liquid or gas by means of a fan or pump.
- Movement of fluid by mechanical force such as fans or pumps.
- Forced downshift
- An automatic transmission system that enables a driver to accelerate rapidly. When the accelerator pedal is fully depressed, the transmission engages a lower gear to give this extra boost. Also called, passing gear. The British term is kickdown.
- Forced-feed lubrication
- A lubrication system used in all modern four-stroke engines, in which an engine-driven pump forces the oil through passages in the engine castings, or through external pipes, to the main areas of stress in the engine
- Forced-induction system
- A system in which either a conventional supercharger or a turbocharger, or even a combination of both, is used to increase intake pressure and force the mixture into the cylinders. Compare Naturally aspirated engine
- Force dry
- The accelerated drying of paint by heat or air movement
- Force Majeure
- Condition in contract that relieves either party from obligations where major unforeseen events prevent compliance with provisions of agreement.
- Ford
-
An automobile produced by the Ford Motor Company which, until 2007, was the second largest car manufacturer after GM; but now has been surpassed by Toyota.
- The 1954 Crestline Skyliner is a milestone car.
- The 1957-59 Skyliner Retractable models are milestone cars.
- The 1955-56 Crown Vic Skyliner models are milestone cars.
- The 1946-48 Sportsman models are milestone cars.
- The 1955-57 and 1958-60 Thunderbird models are milestone cars.
It includes the following models
- Aerostar (1986-97)
- Aspire (1994-97)
- Bronco (1966-96)
- Bronco II (1984-90)
- Club Wagon (1961-98)
- Contour (1995-2000)
- Country Squire (1950-91)
- Crown Victoria (1955-56, 1978-2008)
- Econoline (1961-2008)
- Edge (2007-08)
- Escape (2001-08)
- Escort (1981-2003)
- Excursion (2000-05)
- EXP (1982-88)
- Expedition (1997-2008)
- Expedition EL (2007-08)
- Explorer (1991-2008)
- Explorer Sport (2000-03)
- Explorer Sport Trac (2001-08)
- F150 (1948-2008)
- F250 (1948-2008)
- F350 (1948-2008)
- Festiva (1986-97)
- Five Hundred (2005-07)
- Focus (2000-08)
- Freestar (2004-07)
- Freestyle (2005-07)
- Fusion (2006-08)
- GT (2005-06)
- Model A
- Mustang (1964-08)
- Probe (1989-97)
- Ranger (1983-2008)
- Taurus (1986-2008)
- Taurus X (2008)
- Tempo (1984-94)
- Thunderbird (1955-97, 2002-2005)
- Windstar (1995-2003)
- ZX2 (2001-03)
- Ford
- Submerged stream crossing where tread is reinforced to bear intended traffic.
- Ford fixed orifice tube system
- (FFOT) An air conditioning system that uses an accumulator instead of a receiver-drier and an orifice tube instead of an expansion valve. The accumulator is located at the evaporator outlet. A pressure sensing switch cycles compressor operation
- Fordism
- The Encyclopedia Britannica first called the process of mass production by this name. However, mass production simply evolved in almost every industry at the beginning of the 20th century.
- Fordor
- A word coined by Ford for a 4-door sedan in the 1930s and 1940s.
- Ford-type lug
- A special type of battery connection consisting of a flat lug with nut and bolt between the battery cables and terminal posts. Also called Ford-type terminal
- Ford-type terminal
- A special type of battery connection consisting of a flat lug with nut and bolt between the battery cables and terminal posts. Also called Ford-type lug
- Fore-and-aft flat twin
- A flat-twin motorcycle engine mounted with the cylinders positioned in-line with the frame
- Forecar
- Early three-wheeled vehicle with two-front wheels attached to a motorcycle-based frame. Passengers sat above the front axle
- Forecastle
-
- The raised part of the forward end of a ship’s deck. It is used for the storing paints, tackle, deck stores, tarpaulins, ropes, etc.
- The forward upper portion of the hull, sometimes used for the crew’s quarters.
- Forehand welding
- A style of welding where the heat of the welder is in front of the weld so that the metal is preheated
- Foreign Trade Zones
- Goods subject to duty may be brought into such zones duty-free for transshipment, storage, minor manipulation, and/or sorting. Duty must be paid when/if goods are brought from a zone into any part of the U.S.
- Forepeak bulkhead
- The foremost main transverse watertight bulkhead nearest the bow designed to keep water out of the forward hold in case of bow collision damage. Also called Collision bulkhead
- Fore perpendiculars
- A vertical line at the intersection of the fore side of the stem and the summer load waterline.
- Forge
- To force a piece of hot metal into the desired shape by applying pressure on it (including hammering it) or pushing it through a die.
See
- Forged aluminum
- An engine piston that is formed under tremendous pressure. Forging creates a denser material that is much stronger but more expensive to make.
- Forging
-
- A process (usually involving hammering or squeezing red hot metal) that transforms solid metal into shapes of varying cross-sectional material thickness, often involving heating.
- A piece of forged metal alloy
- Forgiving
- A characteristic of a component or vehicle which overlooks problems or mistakes that a driver might make. For example, a vehicle’s handling may be forgiving in that even if the driver makes small inadvertent steering wheel movements, the vehicle continues to go straight.
- For-Hire Carrier
- A company in the business of transporting freight belonging to others. Compare Private Carrier
- Fork
-
Fork
- The part of the bicycle or motorcycle frame that fits inside the Head tube and holds the front wheel. Generally called the front fork.
- The part of the bicycle frame where Chainstays and Seatstays join to hold the rear axle.
- A shifting device that is U-shaped and moves gears back and forth on the shaft.
- Fork blade
- One of the two parallel curved tubes that hold the front wheel of a bicycle.
- Fork blades
- The two parallel curved tubes that hold the front wheel of a bicycle.
- Fork crown
- The horizontal piece on the upper part of the front fork to which the Fork blades attach on a bicycle.
- Fork ear
- A metal piece which surrounds the front forks of a motorcycle and acts as a fork protector. The Headlight shell is mounted to the protrusions from each protector
- Forked con rod
- A special split connecting rod to take two pistons for uniflow-scavenging two-stroke engines with two pistons per cylinder
- Forked rocker
- A Rocker arm operating two valves with its forked end
- Forked rocker arm
- A Rocker arm operating two valves with its forked end
- Fork Entry
- The openings between deck boards beneath the top deck or beneath the stringer notch to admit forks.
- Fork lift
-
Fork lift
(Lift truck) A vehicle having metal arms extended in front for picking up and moving pallets, crates, or skids. A forklift may have a special attachment on the front for specialized handling of certain products. There are warehouse and rough-terrain forklifts. Also called Hi-Lo®, jeep, or Towmotor®.
- Fork-lift truck
- A small vehicle used for loading in factories, warehouses, docks, etc., with two arms at the front projecting forward which fit into pallets and can be raised and lowered
- Fork mount
- A vertical bar mounted on a roof rack to hold the front forks of a bicycle when the front wheel has been removed. The front wheel is subsequently placed in a U-shaped tray
- Fork rake
- On a bicycle or motorcycle the shortest distance between the front axle and an imaginary line extending through the Head tube downward toward the ground.
See
- Rake.
- Fork tip
- One of the slotted ends of the Fork blades into which the front wheel axle fits on a bicycle.
- Fork tips
- The slotted ends of the Fork blades into which the front wheel axle fits on a bicycle.
- Fork tubes
- On a motorcycle, the long sturdy tubes attached to triple clamps and fitted inside fork sliders.
- Formal hardtop
-
Formal hardtop
The hardtop roofline was a long-lasting fashion hit of the postwar car era. The word formal can be applied to things that are stiffly conservative and follow the established rule. The limousine, being the popular choice of conservative buyers who belonged to the Establishment, was looked upon as a formal motorcar. So when designers combined the lines of these two body styles, the result was the Formal Hardtop. This style has been marketed with two or four doors, canopy and vinyl roofs (full or partial) and conventional or opera-type windows, under various trade names. The distinction between a formal hardtop and plain pillared-hardtop coupe hasn’t always followed a strict rule.
- Former
- A shaped wooden block for use in panel beating, on which a desired shape is produced by hammering.
- Form factor
- A figure of merit that indicates how much rectified current departs from pure (nonpulsating) (DC). A large departure from form factor (pure DC) increases the heating effect of the electric motor and reduces brush life
- Formula I
- A formula according to which racing cars are built for the major Grand Prix races counting for the World Championship
- Formula One
- A formula according to which racing cars are built for the major Grand Prix races counting for the World Championship
- Forsterite
- A crystalline chemical compound in Brake dust created by the action of heat on asbestos
- 49-state car
- A car that complies with U.S. emission standards which are less restrictive than the standards in California.
See
- 49 state car
- A car that complies with U.S. emission standards which are less restrictive than the standards in California.
See
- Forty-nine state car
- A car that complies with U.S. emission standards which are less restrictive than the standards in California.
See
- Forward bias
- Conductive condition that exists when current flows through a Diode.
- Forwarder
- See Freight Forwarder.
- Forwarding agent
- A firm specializing in shipping goods abroad. Payments made for insurance and other expenses are charged to the foreign buyer.
- Forward perpendicular
- A vertical line at the intersection of the fore side of the stem and the summer load waterline
- Forward shift
- From the neutral position, the movement of the commutator brushes in the same direction of rotation
- Fossil fuel
- An energy source formed in the Earth’s crust from decayed organic material. The common fossil fuels are petroleum, coal, and natural gas.
- Foul
-
- To clog or cover (a spark plug) with oil or soot/carbon deposits which can cause a loss of performance and engine misfire.
- To get in the way of another part or obstruct it.
- Fouling
- A situation that takes place when oil or carbon impedes the normal operation of a component. For instance, a spark plug can become fouled by oil so that a spark cannot be formed across the electrodes.
See
- Four-barrel carburetor
-
A carburetor with four Barrels to allow fuel into the manifold. In normal operation, it work like a Dual carburetor by closing off two barrels so that the throttle operates one pair of barrels. At high demand, the second throttle butterfly opens the other two barrels to provide more fuel and thus more power. Usually found on large V-8 engines.
- Four bolt mains
-
Four bolt mains
A term referring to the number of bolts needed to secure each cap to a crankshaft rod. Most engines come with two bolt main; but racing engines have four.
- 4/C
- Abbreviation for Four-color, usually referring to color photographs or slides. A term used in classified advertisements to indicate the availability of pictures of a vehicle.
- Four color
- (4/C) Usually referring to color photographs or slides. A term used in classified advertisements to indicate the availability of pictures of a vehicle.
- Four-cylinder engine
- An engine with four cylinders usually in line; but can also be V-type or horizontally opposed. The in-line type is the most common in most small cars and in larger motorcycles.
- Four-door hardtop
-
Four-door hardtop
This is a four-door car styled to resemble a convertible, but having a rigid top of metal or fiberglass. Buick introduced a totally pillarless design in 1955. A year later most automakers offered equivalent bodies. Four-door hardtops have also been labeled sports sedans and hardtop sedans. By 1976, potential rollover standards and waning popularity had taken their toll. Only a few makes still produced a four-door hard-top and those disappeared soon thereafter.
- Four-door hatchback
-
Four-door hatchback
Essentially unknown among domestic models in the mid-1970s, the four-door hatchback became a popular model as cars grew smaller and front-wheel-drive versions appeared. Styling was similar to the original two-door hatchback, except for two more doors. Luggage was carried in the back of the car itself, loaded through the hatch opening, not in a separate trunk.
- Four-door pillared hardtop
-
Four-door pillared hardtop
Once the true four-door hardtop began to fade away, manufacturers needed another name for their luxury four-doors. Many were styled to look almost like the former pillarless models, with thin or unobtrusive pillars between the doors. Some, in fact, were called thin-pillar hardtops. The distinction between certain pillared hardtops and ordinary (presumably humdrum) sedans occasionally grew hazy.
- Four-door sedan
-
Four-door sedan
If you took the wheels off a car, mounted it on poles and hired two weightlifters (one in front and one in back) to carry you around in it, you’d have a true sedan. Since this idea isn’t very practical, it’s better to use the term for an automobile with a permanent top (affixed by solid pillars) that seats four or more persons, including the driver, on two full-width seats.
- Four-door station wagon
-
Four-door station wagon
Since functionality and adaptability are advantages of station wagons, four-door versions have traditionally been sales leaders. At least they were until cars began to grow smaller. This style usually has lowerable windows in all four doors and fixed rear side glass. The term suburban was almost synonymous with station wagon at one time, but is now more commonly applied to light trucks with similar styling. Station wagons have had many trade names, such as Country Squire (Ford) and Sport Suburban (Plymouth). Quite a few have retained simulated wood paneling, keeping alive the wagon’s origin as a wood-bodied vehicle.
- 442
- A sub-model of the Cutlass model of automobile produced by Oldsmobile. The 1964-70 442 models are milestone cars.
- Four-gas analyzer
- Equipment for testing exhaust gas for hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and oxygen
- Four-link rear suspension
- An independent rear suspension layout, also used on live rear axles, in which each wheel is guided by two control arms, one mounted longitudinally, the other mounted transversely or almost transversely, thus providing lateral location for the axle. A suspension setup that uses 4 rods (or links) to locate an axle. Depending on the arrangement of the links, a panhard rod or watts link may be used to control side to side motion. This type of suspension was used in most American designed rear wheel drive cars built from the 60’s, 70’s, and 80’s.
- Four on the floor
- A Four-speed manual transmission with floor mounted shift rather than on the steering column.
- Four-on-the-floor
- A Four-speed manual transmission with floor mounted shift.
- Four piston caliper
- A disc brake caliper of the fixed type that has two pistons on each side of the disc.
- 4-spd
- Abbreviation for Four-speed, either manual transmission or automatic transmission.
- Four speed
- A transmission which has four forward gears.
- Four-speed
- A transmission which has four forward gears.
- Four-speed gearbox
- A British term for a Four-speed transmission
- Four-speed transmission
- A manual or automatic transmission which has four forward gears. In most instances, the top gear is an overdrive.
- Four-stroke cycle engine
- An engine requiring two complete revolutions of the crankshaft to fire each piston once. The first stroke down (Intake stroke) pulls fuel and air into the combustion chamber. The second stroke up (compression stroke) compresses the mixture. The third stroke down (Power stroke) comes about through the rapid burning of the compressed fuel mixture. The fourth stroke up (exhaust stroke) expels the exhaust gases from the cylinder. It is also called the Otto cycle.
- Fourth
- The highest gear in a four-speed transmission or the second highest in a five-speed transmission.
- Fourth gear
- The highest gear in a four-speed transmission or the second highest in a five-speed transmission.
- Four valve
- An engine which has four valves (two intake and two exhaust) for each cylinder. Multiple valve systems offer better breathing.
- Four-Way Block Pallet
- A pallet with openings at both pallet ends and along pallet sides sufficient to admit hand-pallet jacks; full four-way entry pallet.
- Four Way Stop
- An intersection in which traffic is controlled by a stop sign at each corner. The rules:
- The first arriving vehicle has the right of way after coming to a complete stop.
- In the event that two vehicles arrive at the same time, the vehicle on the right has the right of way.
- Two vehicles directly opposite to each other whose intention is not to turn, may go ahead at the same time.
- Four-way wheel wrench
-
Four-way wheel wrench
A lug wrench shaped in the form an X with a socket at each end. Also called a wheel nut spider.
- Four-wheel alignment
- In most rear-drive vehicles only the front wheels need to have their wheels aligned because the rear wheels are on a fixed axle. However with front-drive vehicles and rear-drive vehicles with Independent suspension, all four wheels need to be aligned.
See
- Four-wheel drift
- A term that describes a cornering situation in which all four tires are operating at large Slip angles so that a car gets into a sideways slide.
- 4WD
- Abbreviation for Four-wheel drive. This term should be distinguished from FWD which is Front-wheel drive.
- Four-wheel drive
-
Four-wheel drive
(4WD) (4×4) A type of drive system in which both front wheels are connected to its own differential and axles, and both back wheels are connected to its own differential and axles. Between these two differentials there is a Transfer case which allows you, in the case of part-time four wheel drive, to switch between Two-wheel drive and four-wheel drive. In full-time four-wheel drive, power is sent to both differentials.
- Four-wheel-drive high
- (4WD Hi) A four-wheel drive, with the final drive ratio the same as when the vehicle is in two-wheel drive.
- Four-wheel-drive low
- (4WD Lo) A separate low-ratio transfer case gear set designed for low-speed operation and maximum traction in difficult terrain. In virtually all systems, engaging 4WD Lo usually requires bringing the vehicle to a complete stop.
- 4WS
- Abbreviation for Four-wheel steering.
- Four wheeler
- Trucker slang for a passenger car or pickup as in ‘Looks like smokey is giving that four wheeler an invitation.’
- Four-wheel steering
- A vehicle where the rear wheels also turn when the front wheels turn to give a sharper and more accurate turn.
- FP
- Abbreviation for Fuel Pump
- FPM
- Abbreviation for Fuel Pump Monitor (in PCM) which monitors Fuel Pump high and low circuits
- FPS system
- An imperial system of units, superseded by the SI (metric) system
- FR
- Abbreviation for frame — The NEMA system of standardization of motor-mounting dimensions
- Fractional-horsepower electric motor
- An Open enclosure electric motor with continuous rating of less than 1 horsepower (hp) at 1700-1800 rpm
- Fractionation
- The process by which saturated hydrocarbons are removed from natural gas and separated into distinct products, or fractions, such as propane, butane, and ethane.
- Fracture
- The breaking apart or tearing of an object due to stress, impact, temperature, pressure, etc.
See
- Frame
-
Frame
- A bridge-like structural load-carrying members of a vehicle that support the engine and body and are in turn supported by the wheels of the vehicle.
- Transverse members that make up the riblike skeleton of a ship.
- (FR) The NEMA system of standardization of electric motor-mounting dimensions
See
- A-frame
- Ash frame
- Backbone frame
- Bicycle frame
- Boss Frame
- Buck Frame
- Cant Frame
- Chassis frame
- Cradle Frame
- Cruciform frame
- Diamond frame
- Door frame
- Double-cradle Frame
- Featherbed Frame
- Floating frame
- Keystone Frame
- Ladder frame
- Ladies’ frame
- License plate frame
- Loop Frame
- Mixte frame
- Mounting frame
- New Werner Frame
- Open Cradle Frame
- Open Frame
- Panting frame
- Perimeter frame
- Platform frame
- Reverse Frame
- Serrated Frame
- Side frame
- Space frame
- Spectacle frame
- Spine Frame
- Stack End Frame
- Stern Frame
- Sub Frame
- Transom frame
- Transverse Frame
- Tube frame
- Tubular backbone frame
- Tubular frame
- Twin-spar Frame
- Twisted frame
- Underslung frame
- Web frame
- X-type frame
- Frame construction
- A type of trailer construction in which the weight of the load is transmitted through the cross members and outriggers directly into the main frame, rather than borne by the sides of the trailer.
- Frame damage
- A type of damage to the body that involves damage to the structural members of the car, usually resulting from collision impact
- Frame-integral
- Another term for unitized body
- Frameless
- A vehicle without a frame such as a Unibody construction
- Frameless window
- A door window which does not have a frame around the three sides (left, right, and top).
- Frame-Off Restoration
- A process of restoring a vehicle where the body shell is removed from the frame. In this process, the car is disabled until all or most of the restoration is completed. In contrast, see Body-On Restoration or Frame-up restoration
- Frame structure
- All parts of the vehicle which contribute to the rigidity of the body, both for unibody designs and for vehicles with a separate chassis
- Frame-up restoration
- A less rigorous restoration than a frame-off in which the car has not been disassembled. Only certain components such as paint, chrome, interior, and maybe some mechanical items having been restored.
- Framework Convention on Climate Change
- (FCCC) An agreement opened for signature at the Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, on June 4, 1992, which has the goal of stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that would prevent significant anthropogenically forced climate change.
- Franchised dealer
- An automotive dealer which sells a particular brand, e.g., Anytown Ford is a franchised dealer for Ford cars and is authorized to sell Ford parts as well as provide service for Ford vehicles.
- Franklin
- A vehicle brand of which all the 1925-48 models except the 1933-34 Olympic Six are classic cars.
- Frazer
- A vehicle brand of which the 1947-50 Manhattan models are milestone cars.
- Frazer Nash
- A vehicle brand of which the 1925-1948 models with required application are classic cars.
- Fred
- (from road riding) a person who has a mishmash of old gear, doesn’t care at all about technology or fashion, didn’t race or follow racing, etc. Often identified by chainring marks on white calf socks. Used by serious roadies to disparage utility cyclists and touring riders, especially after these totally unfashionable freds drop the serious roadies on hills because the serious guys were really posers. According to popular myth, Fred was a well-known grumpy old touring rider, who really was named Fred.
- Free Alongside
- (FAS) Selling term in international trade. Selling party quotes price including delivery of goods alongside overseas vessel at exporting port.
- Free alongside ship
- (f.a.s.) The value of a commodity at the port of exportation, generally including the purchase price plus all charges incurred in placing the commodity alongside the carrier at the port of exportation.
- Free-astray
- A shipment that is mis-routed or unloaded at the wrong terminal and is billed and forwarded to the correct terminal free of charge.
- Freeboard
-
- The distance from the waterline to the upper surface of the freeboard deck at side.
- The vertical distance from the upper watertight deck to waterline, when the ship is fully loaded.
- Freeboard Mark
- See Plimsoll mark.
- Free electrons
- Electrons in the outer orbits around the nucleus of the atom. They can be moved out of orbit comparatively easy.
- Freehub
-
Freehub
The center part of a bicycle wheel to which the rear sprockets are attached and from which the spokes radiate to the rim.
- Freeing port
- An opening in the lower portion of a bulwark, which allows deck water to drain overboard
- Free length
- The length of a spring, especially a valve spring, when no downward pressure is exerted on it
- Free Machining
- The property that makes machining easy because of the forming of small chips, a characteristic imparted to steel by sulfur, etc.
- Free on board
- (f.o.b.) (FOB) A sales transaction in which the seller makes the product available for pick up at a specified port or terminal at a specified price and the buyer pays for the subsequent transportation and insurance.
- Free pedal play
- The distance the Clutch pedal can be depressed before it begins to disengage the clutch. Generally about 19-25 mm (0.5-1 inch) free pedal play is normal to be sure that slight resting of the foot on the pedal will not disengage the clutch. Without free pedal play, the throwout bearings and the clutch might wear out.
- Free play
-
- The amount of looseness in some component before it engages.
- The amount of travel before any action takes place. In a brake pedal, it is the distance the pedal moves before the pistons in the master cylinder are actuated.
- British term for Lash.
See
- Free radius
- Measurement in inches (or millimetres) from the wheel axle centerline to the top of the tire when inflated. (The radius that is not under load.) Also called unloaded radius.
- Free-revving
- The ability of an engine to accelerate quickly to high engine speeds
- Freeride bike
- A type of mountain bicycle designed to ride the most technical and punishing of downhill trails; features include long-travel (6 to 8 inches), dual suspension, and components made for ultimate strength
- Free rolling wheel
- A non-powered wheel position on a vehicle, such as steering axle, tag axle or trailer wheel positions.
- Free-running speed
- The speed that a vehicle will reach where there is a constant power or force produced by the engine which is equal to all resistance
- Free shape
- A design shape of a component which is governed only by stylistic or functional requirements.
- Free time
- The period freight will be held before storage charges are applied. The period allowed for the owner to accept delivery before storage charges begin to accrue.
- Free Trade Agreement of the Americas
- (FTAA) An effort to unite the economies of the Western Hemisphere into a single free trade arrangement. The Heads of State of the 34 democracies in the region agreed to construct a Free Trade Area of the Americas and to complete negotiations for the agreement by 2005.
- Freeway
- A multiple lane highway without toll charges. All exits and entrances are made through overpasses and Cloverleafs. Because there is no direct cross traffic, speeds can be over 100 km/h
- Freeway bar
- A component on a motorcycle which is a rod with a footrest on each end. The rod is mounted ahead of the engine to provide an alternate place to position the rider’s feet.
- Freewheel
-
- Usually refers to the action of a vehicle on a downgrade when the Overdrive over-running clutch is slipping with a resultant loss of engine braking. This condition will occur only after the overdrive unit is engaged but before the Balk ring has activated the Planetary gearset.
-
Freewheel
The removable cluster of gears at the hub of the rear wheel of a bicycle. Usually there are five or more gears. It also contains a Ratcheting mechanism inside that allows the wheel to rotate forward while the pedals, chain, and gear Sprockets remain still or move in reverse. The rear derailleur moves the chain from one gear to the other to change the Gear ratio. The other end of the chain wraps around the Chainwheel. The freewheel threads onto the hub while the newer style of gear cluster (cassette) slides onto the hub.
- Freewheel hub
-
- A type of hub fitted to the front axle of some four-wheel drive vehicles, in which the drive to the front wheels can be disconnected when the front axle is not being driven.
- Older type of a bicycle rear hub designed to accept the freewheel type of gear cluster. The freewheel hub is threaded to accept the freewheel cluster.
- Freewheeling
-
- In a motorized vehicle, the illegal coasting by putting the transmission in neutral or disengaging the clutch.
- Continued rotation of Magnetic clutch on automotive compressor when clutch is disengaged.
- Freewheeling hub
- A type of hub fitted to the front axle of some four-wheel drive vehicles, in which the drive to the front wheels can be disconnected when the front axle is not being driven
- Freeze
-
- To reach a temperature in which a liquid turns into a solid.
See
- To adhere firmly.
- To stop.
- An American (not Canadian) term for an engine which has seized. To an American, My engine is frozen means seized because it has run out of oil and overheated so that pistons expanded and won’t move in the cylinder. To a Canadian, it means the coolant won’t flow or the engine won’t warm up.
- To reach a temperature in which a liquid turns into a solid.
- Freeze drying
- Uses liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide to turn fresh food into long lasting, frozen food. It is also referred to as fast food freezing and cryogenic food freezing.
- Freeze plug
- A removable plug on the block which can pop out should the coolant in the block freeze and expand. Sometimes a plug will develop a leak and will need replacing. Also called Expansion plug. The British term is Core plug.
- Freezer alarm
- A bell or buzzer used in many freezers which sounds an alarm when freezer temperature rises above safe limit.
- Freezer burn
- Condition applied to food which has not been properly wrapped and that has become hard, dry, and discolored.
- Freeze-up
-
- The formation of ice in the refrigerant control device which may stop the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator.
- Frost formation on an evaporator which may stop the airflow through the evaporator.
- The failure of a unit to operate properly because of the formation of ice at the expansion valve orifice or on the evaporator coils or fins
- Freezgard
- A product composed of approximately 25 percent magnesium chloride and 75 percent water that is used as an alternative to road salt or to pre-wet salt
- Freezing
-
- When two parts that are rubbing together heat up and force the Lubricant out of the area. As they create heat, they will expand and tear bits of metal from each other, then stick and refuse to move.
- Change of state from liquid to solid.
- Freezing point
- Temperature at which a liquid will solidify upon removal of heat. The freezing temperature for water is 0°C at standard atmospheric pressure.
- Freight assembly center
- (FAC) A large service center that sorts, loads, routes and dispatches freight into the carrier’s system.
- Freight bill
-
- A document that describes the freight, identifies the name of the consignee and shipper, shows the point of origin and destination, the pieces and weight of the freight, and the amount of freight charges.
- An invoice for transportation charges generated when a load is delivered.
- Freight Charge
- Compensation paid to the shipping company by the client for transportation services performed.
- Freight Cost
- This is the compensation paid to the contracted carrier by the shipping company for the transportation services performed.
- Freight flow
- The routing plan that directs the transport freight over a relatively long distance, usually between cities and/or service centers and FACs.
- Freight Forwarder
-
- An individual/company that accepts less-than truckload (LTL) shipments and consolidates them into truckload lots on a for-hire basis.
- An agent who helps expedite shipments by preparing the necessary documents/making other arrangements for moving freight.
- Freightshaker
- Trucker slang for a Freightliner® truck as in ‘We’re gonna buy all new freightshakers next year.’
- Frenching
- The customizing process of creating smooth curve shaping around the headlights, tail lights, license plate frames, etc. so that the actual lights, etc. recede a little towards the interior of the panel opening and the chrome bezel or other surround looks as though it is part of the body panel.
See
- French valve
- A Presta valve.
- Freon
-
- Trade name for a family of synthetic chemical refrigerants manufactured by E. I. du Pont de Nemours & Co., Inc.
- A gas used as the cooling medium in older air conditioning and refrigeration systems. Usually called freon-12 or R-12. It has been replaced in automobiles with a new coolant designated 134A.
- Freon-12
- A gas used as the cooling medium in older air conditioning and refrigeration systems. It has been replaced in automobiles with a new coolant designated 134A.
- Frequency
-
- In relation to a radio station, number of cycles per second expressed in hertz at which it broadcasts.
- The number of times a particular event is repeated.
- The number of times that a signal occurs, or repeats, in cycles per second indicated by the notation Hz or hertz.
- Frequency and pulse-width modulation circuit
- A circuit for varying the current into a motor and therefore the torque output. Sometimes called a variable frequency inverter.
- Frequency Modulation
- (FM) A term used to describe a type of radio frequency where the frequency of the wave changes rather than the amplitude.
See
- Frequency scan button
- A radio button which, when pressed, causes the tuner to scan the frequencies of stations with sufficient signal strength and plays that station for about 5 seconds before going to the next one. When the driver or passenger wants to listen to the currently played selection, he can press the same button (or a different one) to select that station. Often called a scan button.
- Frequency valve
-
- A valve located in the fuel distributor of some vehicles with a continuous injection system and catalytic converter. This valve continually adjusts the air/fuel ratio to varying engine operating conditions, because it is controlled by a voltage signal supplied by the oxygen sensor and by an ECM.
- In Bosch CIS, a device that regulates pressure in the lower chamber of the differential-pressure valve, in response to a signal from the lambda (oxygen) sensor. Also called Lambda valve (Bosch’s term) or a Timing valve
- Fresh feed input
- Represents input of material (crude oil, unfinished oils, natural gas liquids, other hydrocarbons and oxygenates or finished products) to processing units at a refinery that is being processed (input) into a particular unit for the first time. Examples: (1) Unfinished oils coming out of a crude oil distillation unit which are input into a catalytic cracking unit are considered fresh feed to the catalytic cracking unit. (2) Unfinished oils coming out of a catalytic cracking unit being looped back into the same catalytic cracking unit to be reprocessed are not considered fresh feed.
- Fresh feeds
- Crude oil or petroleum distillates that are being fed to processing units for the first time.
- Fretting corrosion
-
- Corrosion occurring where two surfaces are in contact and friction results, e.g., at mechanical joints in vibrating structures
- Corrosion occurring when vibration causes a stainless fastener to continually rub against another surface, resulting in the passive oxide film on stainless rubbing off. Fretting corrosion might occur in high tensile fasteners such as martensitic stainless.
- Friction
- The resistance to movement between any two objects when placed in contact with each other. Friction causes wear and heat. In an engine, it robs it of some of its potential power. Friction is not constant but depends on the materials, type of surface finish, amount of pressure holding the two objects together, and the relative amount of movement between the objects. Lubrication like oil, Grease, and other materials like graphite reduce friction.
- Friction bearing
- A bearing made of Babbitt, Bronze, etc. There are no moving parts (like an Antifriction bearing which has ball bearings). The smooth inner surface of the babbitt insert and the smooth surface of the shaft rub or slide against each other. To avoid disintegration, the bearing must use lubrication (i.e., Wet friction). Friction bearings are less expensive and cheaper to service than Antifriction bearings. Also called plain bearing.
- Friction clutch
- A conventional clutch which transmits the power of the drive by mechanical friction, as opposed to a fluid coupling
- Friction drive
- A method of power transmission used on early cars where power is transmitted from a driving to a driven wheel by means of pressing one wheel against another at a right angle.
- Friction horsepower
- (FHP) The amount of power consumed by an engine in driving itself. It includes the power absorbed in mechanical friction and in driving auxiliaries plus, in the case of four-stroke engines, some pumping power.
- Friction lining
- Wear-resistant friction material used for clutch and brake linings
- Friction material
- A blend of substances with a relatively consistent friction coefficient over a wide range of conditions. The friction materials used in automotive brakes are organic, metallic, semi-metallic, and synthetic.
- Friction modifier
-
- A substance which enhances the ability of oil to remain slippery. In most SH and SJ series oil, friction modifiers have been added to improve engine starting and prolong engine life. However, in engines with a Wet clutch (i.e., the engine oil lubricates the clutch plates) such as motorcycle engines, oils with friction modifiers can cause the clutch to slip and may force the premature replacement of the clutch plates.
- Additives used to alter the friction coefficient of a brake lining material
- Friction plate
- A drive plate of a clutch to which the friction lining is attached
- Friction shifters
- Conventional (non-index) levers of a bicycle that retain their position through the use of friction washers.
- Friction shock absorber
- A shock absorber in which friction discs are inserted at the point where the two arms are joined, now no longer used in car suspensions
- Friction welding
- The type of weld in which the necessary welding heat is generated by revolving one part against another part under very heavy pressure. When melting has occurred at the interface, pressure is maintained to consolidate the weld during cooling of the material
- Frogeye
- A nickname for the Series I Austin-Healey Sprite produced from 1958-1962, which had the headlights projecting above the hood line
- Frontage road
- A road that parallels a larger highway and provides access to communities, stores, etc. Frontage/service roads limit the number of entrance and exit points onto a major roadway, reducing conflicts and improving safety.
- Front apron
- The panel behind and below the front bumper, joining the bottom ends of the Front fenders
- Front axle
- The most forward axle used for steering. Also called steer axle. The axle to which the front wheels are attached
- Front-axle/rear-axle split
- A dual-circuit braking system in which one circuit brakes only the front axle while the other circuit brakes only the rear axle.
- Front-axle and rear-axle split
- A dual-circuit braking system in which each circuit brakes both the front axle and the rear axle
- Front derailleur
-
Front derailleur
A bicycle component that causes a change in the gear ratio by pushing the chain from one front chainrings to the other
- Front derailleur braze on
- A Braze on with a tab that is found on the seat tube of a Bicycle frame so that the derailleur clamp which encircles the seat tube is eliminated.
- Front derailleur clamp on
- A clamp or band attached to the front derailleur to permit its installation around the seat tube of a Bicycle frame.
- Front door
- Trucker slang for the lead rig in convoy of trucks as in ‘Who’s gonna run front door and be bear bait tonight?’
- Front end
- Body area incorporating the leading edge of the Fenders, the headlights, Radiator grille and bumper, i.e., the full area that makes up the frontal appearance of the car
- Front End Loader
- An off-road vehicle, with either a forked loading device in front or a wide bucket in front.
- Front engine
- A vehicle with its engine located at the front of a vehicle above the front suspension. This is the most common layout, which may be combined with either rear-wheel or front-wheel drive.
- Front fender
- Body section covering the front wheels, originally separate; but now in most cars faired in and part of the body shell
- Front fork
- On a motorcycle, the spring and damping device that holds the front wheel in place.
See
- Fork.
- Front forks
-
See
- Fork.
- Front hub
-
Front hub
On a bicycle, the front wheel’s center from which the spokes radiate.
- Front-Loader
- A refuse truck that is loaded at the front usually has hydraulic arms that lift dumpsters over the cab dumping their contents into a bin with some kind of compacting mechanism. Arms must be included in truck length.
- Front nose section
- The front section of a car’s body that uses one single structure to make up the front end, i.e., including the Radiator grille surround, both Fenders, front apron, etc.
- Front panel
- A panel joining the Front fender and forming a mounting for the headlights, Grille, and air ducts into the engine compartment, which is often identical with the front apron where no separate apron is fitted below the front panel.
See
- Front pipe
- The first section of the exhaust system from the exhaust manifold to the Silencer (or front silencer where there are two).
See
- Front-seat
- The closed position of a stem type service valve to isolate the compressor. The system should never be operated with the valves in this position
- Front silencer
- First and main Silencer in an exhaust system where there are two silencers.
- Front spoiler
- The Air deflector on the front of a car, aerodynamically designed to cut the wind resistance around the car, for improved handling control, stability, traction, and better fuel economy
- Front suspension
- The springs, shock absorbers, linkages, etc. which support the front wheels.
- Front track
- The distance between the center of the left front wheel and the center of the right front wheel when the vehicle is set to its normal ride height and wheel alignment specifications. It is not necessarily the same as the rear track
- Front triangle
- Actually a quadrilateral with one short side, it is the section of a bicycle frame that consists of the Head tube, the Top tube, the Seat tube, and the Down tube. Also called main triangle.
- Front wheel carrier
- A U-shaped tray into which the front wheel of a bicycle is mounted when the rest of the bike is secured to a Fork mount bike rack
- Front-wheel drive
- (FWD) A vehicle that is pulled by its front wheels rather than being pushed by its rear wheels. The driveshaft and center floor hump is eliminated in front-wheel drive cars. The engine is located over the driving wheels so that it gains better traction in snow. Wear on the front tires can be severe.
- Front wheel tire clearance
- The distance between the tire and the closest point on the vehicle laterally, longitudinally and vertically, checked lock to lock and all intermediate points.
- Front wing
- British term for Front fender
- Frost back
- Condition in which liquid refrigerant flows from evaporator into suction line; usually indicated by sweating or frosting of the suction line.
- Frost free refrigerator
- Refrigerated cabinet which operates with an automatic defrost during each cycle.
- Frost heaves
- A condition of a roadway in which frost buildup beneath the surface causes the pavement to bulge
- Frosting type evaporator
- Refrigerating system which maintains the evaporator at frosting temperatures during all phases of cycle.
- Frozen
-
- Water in its solid state.
- Seized (as in machine parts) due to lack of lubrication. The term freeze-up is often applied to this situation.
- FRP
-
- Abbreviation for Fuel Rail Pressure
- Abbreviation for fiber reinforced plastic. Continuous mat or woven fibers impregnated with plastic resins to form a lightweight but extremely strong solid. These plastics are stronger per pound than steel. Commonly used fibers are aramid (kevlar), carbon fiber, nomex, and glass. These fibers are used alternatively to provide various levels of strength and weight.
- Frustum
-
Frustum
- The remainder of a pyramid or cone when the top portion is removed parallel to the base.
- The wide end of a bevel gear
FshAn
abbreviation used in classified advertisement indicating full service history is available.
- FT
- Abbreviation for Fuel Trim
- FTA
- Abbreviation for Canada-U.S. Free Trade Agreement.
- FTAA
- Abbreviation for Free Trade Agreement of the Americas.
- FTP test cycle
- An American method of testing automotive emissions for compliance with emission standards by simulating typical driving conditions. This system differs from other test cycles such as the European ECE test, so that the results cannot be compared
- Fuel
-
- Any material substance that can be consumed to supply heat or power. Included are petroleum (gasoline and diesel), coal, and natural gas (CNG, LPG), and other consumable materials, such as uranium, biomass, and hydrogen.
- A material used to create heat or power through chemical conversion in processes such as burning or electrochemistry.
- A combustible material used to produce energy. One of the essential factors in a Combustion engine (Fuel, Air, Proper proportion of mixture, compression, timing, spark).
See
- Air And Fuel
- air-fuel ratio
- Alcohol Fuel
- Alternative Fuel
- Aviation fuel
- Boiler Fuel
- Bunker Fuels
- Ceramic Fuel
- Clean Fuel
- Deceleration fuel cut-off
- Diesel fuel
- Domestic Fuel
- Early fuel evaporation system
- Electric fuel pump
- Electronic fuel injection
- EPA fuel economy
- in-line fuel filter
- Injection Fuel
- integral fuel filter
- Jet Fuel
- Kerosene Jet Fuel
- L-jetronic fuel injection system
- Low fuel indicator
- Low Sulfur Diesel Fuel
- Naphtha-Type Jet Fuel
- Near Neat Fuel
- Neat Alcohol Fuel
- Neat Fuel
- Nonrenewable Fuels
- Number One Diesel Fuel
- Number Two Diesel Fuel
- Oxygenated Fuel
- Petroleum Fuel
- Port fuel injection
- Primary Fuels
- Process Fuel
- Proper proportion of air and fuel
- Refinery Fuel
- Temporarily Discharged Fuel
- Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel Fuel
- Fuel accumulator
-
- A device in the K-Jetronicfuel injection system which serves to absorb the initial pressure surge when a fuel pump starts
- A diaphragm unit which helps maintain residual fuel pressure for hot starting on CIS type fuel system
- Fuel additive
- A chemical preparation which is added to fuel to improve and maintain its properties. Detergents and corrosion inhibitors are examples of gasoline additives.
- Fuel advance system
- Advances fuel delivery during cold starts on GM vehicle. Consists of a thermal-sensitive Solenoid on the intake manifold which sends a signal to the HPCA terminal, which opens a ball-check valve on top of the injection pump housing. With pump housing pressure reduced, the timing mechanism has less resistance to overcome and operates earlier, advancing fuel delivery 3 degrees
- Fuel-air mixture
-
- A combination of Vaporized fuel and air which is brought into the cylinder through the carburetor or fuel injectors. When it is compressed and ignited, it produces the power needed to drive the engine.
- A mist consisting of fuel and air that’s compressed in the cylinders and ignited to drive the pistons in a car’s engine.
- Fuel-air ratio
- The amount of fuel in comparison with the amount of air. This is the reciprocal of the air-fuel ratio.
- Fuel burner
- Competition vehicle with an engine set up to burn alcohol, nitro, etc. mixture instead of standard pump gasoline. Also called fueller.
- Fuel cap
-
Fuel cap
A vented covering on the top of the tube leading to the fuel tank. Also called gas cap.
- Fuel cell
-
- A galvanic cell in which the oxidation of a fuel (e.g., methanol) is used to produce electricity.
- A cell that converts chemical energy directly into electric energy, with electric power being produced as part of a chemical reaction between the electrolyte and a fuel such as kerosene or industrial fuel gas.
- An electrochemical power plant (no moving parts) that creates electrical current from hydrogen and oxygen that is passed over a catalyst, usually a microscopically thin sheet of platinum. The electrical current is then fed directly to an electric motor for propulsion. Fuel cells differ from conventional electrical cells in that the active materials such as fuel and oxygen are not contained within the cell but are supplied from outside. It does not contain an intermediate heat cycle, as do most other electrical generation techniques. The only by product of a fuel cell’s operation is water, which is pure enough to drink. These cells were first used by NASA in the 1960’s for power generation in space capsules. The high price of fuel cell technology has limited the growth of their implementation, but now cells are being used to generate power in hospitals, and to propel vehicles.
- Fuel cock
- A tap which can allow or restrict the flow of gasoline from the gas tank to the carburetor. An essential item on a motorcycle with gravity fed fuel (i.e., no fuel pump) because if the fuel cock is left on after the engine is shut down, there is the possibility that gasoline could leak past the Needle and seat in the carburetor so that the overflow in the float bowl will make its way into the cylinder and wash the walls and dilute the oil
- Fuel computer
- A device which continuously displays the amount of fuel used over the distance since last set.
- Fuel consumption
- The amount of fuel used, expressed in miles per gallon in Britain and the USA, whereas the international measure is litres per 100 kilometres. The US term is fuel mileage.
- Fuel consumption indicator
- An instrument using a Flowmeter to indicate mpg or litres/100 km at any given moment on a journey
- Fuel Control
- Device designed to regulate the fuel supply to the controlled equipment. These may be manual, semi-automatic or automatic.
- Fuel cycle
- The entire set of sequential processes or stages involved in the utilization of fuel, including extraction in its native form, transformation (converting it to a useful product), transportation to market, and combustion (i.e., consuming it at its final destination). Emissions generally occur at each stage of the fuel cycle.
- Fuel distributor
-
- A device constituting the mixture control unit together with the airflow sensor.
- On Bosch CIS, the device that supplies the injection with pressurized fuel in proportion to air volume, measured by the airflow sensor plate. The fuel distributor houses the control plunger and the differential-pressure valves. All fuel metering takes place inside the fuel distributor
- The component which feeds fuel to the individual engine cylinders corresponding to the air flow rate metered by the air flow sensor on CIS system
- Fuel economy
- The number of litres used per 100 kilometres of driving (a lower number is better); or the number of miles driven divided by the number of gallons used (a higher number is better).
- Fuel efficiency
- Although this factor is similar to fuel economy, it differs in that fuel efficiency involves getting the most amount of energy from an amount of fuel. It answers the question, ‘What percent of the fuel does this engine burn?’
- Fuel ethanol
- (C2H5OH) An anhydrous alcohol (ethanol with less than 1% water) intended for gasoline blending as described in the Oxygenates definition.
- Fuel filler flap
- A piece of rubber about 4′ square and very thin, which is located behind the filler door. When the door is opened, the flap falls down to protect the body from the fuel nozzle.
- Fuel filler neck
- The upper end of the fuel filler tube leading down to the fuel tank, which accepts the fuel hose nozzle at the Gas station
- Fuel filter
-
Fuel filter
A device that removes impurities (dirt and water) from the fuel before it gets to the carburetor or injection system. Filters may be made of metal or plastic screen, paper, or gauze. They are usually found near the carburetor in the fuel line that comes from the fuel pump (in-line fuel filter), or inside the carburetor (integral fuel filter) or within the fuel pump or fuel tank. These units must be cleaned or replaced on a regular basis, usually once a year or they will become clogged and restrict fuel to the carburetor. Without a filter, the jets and orifices in the carburetor will become clogged.
- Fuel gas compressor
- A pump or machine for reducing the volume and increasing the pressure of fuel gas.
- Fuel gauge
- An instrument, usually located on the dashboard or center console, which indicates the amount of fuel in the fuel tank. Most gauges have a Needle which fluctuates between E (empty) and F (full). Others show a digital readout of how many gallons or litres left in the tank. Also called gas gauge.
- Fuel-injected engine
- A gasoline engine with a fuel injection system rather than a carburetor.
- Fuel injection
-
Fuel Injection System
(FI) A fuel system that uses no carburetor but sprays fuel either directly into the cylinders or into the intake manifold just ahead of the cylinders. It uses an electronic sensing device to deliver the correct amount into the combustion chamber. Throttle-body injection locates the injector(s) centrally in the throttle-body housing, while Port injection allocates at least one injector for each cylinder near its Intake port.
- Fuel injection pump
-
- A pump which receives fuel from the fuel tank (often through the fuel-feed pump in the case of diesel engines) and delivers it under pressure to the injectors
- A pump on diesel engines that sends fuel to its mini-pumps, and from there to the fuel injector nozzles.
- Fuel injector
-
Fuel injector
- A special nozzle which sprays the proper amount of gasoline or diesel fuel into the inlet ports, either directly into the combustion chamber or into a pre-chamber in response to signals from an electronic sensing device.
- In all fuel-injection system (except Bosch CIS, CIS/Lambda, and CIS-E systems), a spring loaded, Solenoid (electromagnetic) valve which delivers fuel into the intake manifold, in response to electrical signals from the control module in the CIS, etc. System, the injector is simply a spring-loaded, pressure sensitive valve which opens at a preset value
- Fuel injector nozzle
- The device that works like a hypodermic Needle to inject the proper amount of fuel into the combustion chamber in response to signals from an electronic sensing device on cars with fuel injection systems. It receive fuel at low pressure and shoot it into the engine cylinders at predetermined intervals under higher pressure. Also called fuel injector valve or just fuel injector.
- Fuel line
- The metal, plastic, or rubber hose or pipe through which the fuel passes from the fuel tank to the fuel pump to the carburetor or fuel injector nozzle.
- Fuel metering sensor
-
Fuel metering sensor
A motor detection device on a carburetor which closes or opens a fuel-metering port to regulate fuel mixture, keeping the air-fuel ratio at exactly 14.61 (stoichiometric) at all times.
- Fuel mileage
- A measurement or calculation of the number of miles per amount of fuel — usually measured in miles per gallon.
- Fuel mixture
- A mixture of gasoline and air. An average mixture, by weight, would contain 16 parts of air to one part of gasoline.
- Fuel oil
-
- Kerosene or any hydrocarbon oil as specified by U.S. Department of Commerce Commercial Standard CS1 2 or ASTM D296, or the Canadian Government Specification Board, 3-GP-28, and having a flash point not less than 38°C.
- A liquid petroleum product less volatile than gasoline, used as an energy source. Fuel oil includes distillate fuel oil (No. 1, No. 2, and No. 4), and residual fuel oil (No. 5 and No. 6).
- The heavy distillates from the oil refining process; used as fuel for power stations and marine boilers.
- Fuel oil types
- There are several designated types of fuel oil such as:
- No. 1 diesel fuel: A light distillate fuel oil that has a distillation temperature of 288°C at the 90-percent recovery point and meets the specifications defined in ASTM Specification D 975. It is used in high speed diesel engines generally operated under frequent speed and load changes, such as those in city buses and similar vehicles. See No. 1 distillate below.
- No. 1 distillate: A light petroleum distillate that can be used as either a diesel fuel: (see No. 1 diesel fuel above) or a fuel oil: (see No. 1 fuel oil: (below).
- No. 1 fuel oil: A light distillate fuel oil that has distillation temperatures of 204°C at the 10-percent recovery point and 288°C at the 90-percent recovery point and meets the specifications defined in ASTM Specification D 396. It is used primarily as fuel for portable outdoor stoves and portable outdoor heaters. See No. 1 Distillate above.
- No. 2 diesel fuel: A distillate fuel oil that has a distillation temperature of 338°C at the 90-percent recovery point and meets the specifications defined in ASTM Specification D 975. It is used in high-speed diesel engines that are generally operated under uniform speed and load conditions, such as those in railroad locomotives, trucks, and automobiles. See No. 2 Distillate below.
- No. 2 distillate: A petroleum distillate that can be used as either a diesel fuel: (see No. 2 diesel fuel above) or a fuel oil: (see No. 2 fuel oil below).
- No. 2 fuel oil: (heating oil) A distillate fuel oil that has a distillation temperature of 338°C at the 90-percent recovery point and meets the specifications defined in ASTM Specification D 396. It is used in atomizing type burners for domestic heating or for moderate capacity commercial/industrial burner units. See No. 2 Distillate above.
- No. 2 fuel oil and No. 2 diesel sold to consumers for all other end uses: Those consumers who purchase fuel oil or diesel fuel for their own use including: commercial/institutional buildings: (including apartment buildings), manufacturing and nonmanufacturing establishments, farms: (including farm houses), motor vehicles, commercial or private boats, military, governments, electric utilities, railroads, construction, logging or any other nonresidential end-use purpose.
- No. 2 fuel oil sold to private homes for heating: Private household customers who purchase fuel oil for the specific purpose of heating their home, water heating, cooking, etc., excluding farm houses, farming and apartment buildings.
- No. 4 fuel oil: A distillate fuel oil made by blending distillate fuel oil and residual fuel oil stocks. It conforms with ASTM Specification D 396 or Federal Specification VV-F-815C and is used extensively in industrial plants and in commercial burner installations that are not equipped with preheating facilities. It also includes No. 4 diesel fuel used for low- and medium-speed diesel engines and conforms to ASTM Specification D 975.
- No. 5 and no. 6 fuel oil sold directly to the ultimate consumer: Includes ships, mines, smelters, manufacturing plants, electric utilities, drilling, railroad.
- No. 5 and no. 6 fuel oil sold to refiners or other dealers who will resale the product: Includes all volumes of No. 5 and No. 6 fuel oil purchased by a trade or business with the intent of reselling the product to the ultimate consumers.
- Fuel petcock
- An on-off valve located at the bottom of a motorcycle fuel tank. It may have a filter screen and sediment bowl and sometimes provides a reserve fuel supply.
- Fuel pressure
- The pressure under which fuel is delivered to the injectors by the fuel pump, governed by the pressure regulator
- Fuel pressure regulator
-
Fuel pressure regulator
A spring-loaded pressure-activated diaphragm valve that maintains the pressure in a fuel system to a pre-set value above manifold pressure, particularly in a fuel injection system and meters unused fuel back to the fuel tank.
- Fuel pump
- A vacuum device, operated either mechanically or electrically, that is used to draw gasoline from the tank and sends it into the carburetor or fuel injector nozzles. Mechanical pumps have a Rocker arm that is activated by a cam on the camshaft; the arm causes a diaphragm to move up and down, thus pulling the gas through the pump. Some electrical pumps have a rocker arm which is activated electrically and does the same thing as the mechanical pump. Other electrical pumps are located at the bottom of the fuel tank and push the fuel through the fuel lines.
- Fuel pump filter
-
-
VW Fuel pump filter
A filter screen built into the fuel pump itself as used on VW Beetles with a mechanical fuel pump.
-
screw-on fuel pump filter
A screw-on canister holding a replaceable pleated paper filter. The canister is mounted onto the base of a fuel pump
-
- Fuel pump relay
- An electric switch which activates the fuel pump when the engine is cranked and when the engine is running.
- Fuel pump shut-off switch
- A switch which shuts off the electric fuel pump and fuel to the engine in the event of a major collision
- Fuel pump switch
- A switch which shuts off the electric fuel pump and fuel to the engine in the event of a major collision
- Fuel rail
- A manifold tube feeding the injectors in a fuel injection system. A special manifold designed to provide a large reservoir of pressurized fuel for the fuel injectors, which are attached between the rail and the intake runners or the cylinder head. The fuel rail also serves as a mounting place for the fuel damper (if equipped) and the fuel pressure regulator
- Fuel return line
- A pipe returning surplus fuel to the tank from the carburetor(s) or to the inlet side of the injector pump
- Fuels solvent deasphalting
- A refining process for removing asphalt compounds from petroleum fractions, such as reduced crude oil. The recovered stream from this process is used to produce fuel products.
- Fuel stabilizer
- A chemical which is added to gasoline to prevent it from becoming stale. Gasoline, diesel, or heating fuel reacts with oxygen in the atmosphere and leave behind a varnish-like film or gum residue. While some fuel contains an oxidation inhibitor which allows it to be stored for up to three months, other fuels don’t have this inhibitor. Stale gasoline can clog fuel lines, carburetors, and injectors. A good fuel stabilizer can lengthen fuel’s useful life.
- Fuel starvation
- The failure of the fuel system to supply sufficient fuel to allow the engine to run properly, due to a blockage or vapor lock or malfunction of the fuel pump.
- Fuel supply
- The delivery of fuel to the carburetor or injection system
- Fuel system
- A system that stores, cleans, and delivers the fuel to the engine in proper quantities to meet the varying needs that arise as you drive. It is made up of the fuel tank, fuel lines, fuel pump, fuel filter, and carburetor or the fuel injection system.
- Fuel tank
-
Fuel tank
The storage compartment, under the trunk in most cars, that holds the fuel for the vehicle. Also called the gas tank.
- Fuel tank sender
- A level sensor in the gas tank which sends information about the amount of remaining fuel.
- Fuel tank vapor valve
- A valve mounted in the top of the fuel tank. Vents excess vapor and pressure from the fuel tank into the evaporative emission control system
- Fuel utilization
- In fuel cells, the fraction of the fuel or oxidant that enters the cell that reacts electrochemically.
- Fuel-vacuum separator
- Used to filter waxy hydrocarbons from the carburetor ported vacuum to protect the vacuum delay and distributor vacuum controls
- Fuel vapor
-
- Atomized air/fuel mixture heated in the engine, ready for combustion
- Fumes given off by gasoline
- Fuel vapor recirculation system
- An emission system which traps the excess gasoline vapor, condenses it back to liquid form, and then sends it back to the gasoline tank. Also called evaporative emission control system
- Fuel vapor recovery system
- (FVR) a valve responsible for venting excess fuel vapor and pressure from the fuel system to the EEC system
- Fugitive emissions
- Unintended leaks of gas from the processing, transmission, and/or transportation of fossil fuels.
- Fulcrum pin
- A pin which acts as a pivot, such as a kingpin
- Fulcrum ring
-
Fulcrum ring
One of two rings on either side of a Clutch diaphragm spring on which it pivots.
See
- Full Annealing
- Annealing a ferrous alloy by austenitizing and then cooling slowly through the transformation range.
- Full body diameter
- A screw or bolt where the shoulder diameter is the same as the outside or major diameter of the threaded portion.
- Full bore
-
- A term expressing top speed or full throttle.
- A colloquial term used by vehicle salesmen to express the sale of a vehicle for the full sticker price with no discount.
- Full cam
- A type of camshaft for race car engines which increases lift of valve, speed of valve opening and closing, length of time valve is held open, etc. Also called Race cam, Three-quarter cam, or Semi-race cam, depending upon design
- Full cap
- A condition of retreading where new tread rubber is added to the buffed Casing, and covers the crown and shoulder areas.
- Full Coverage Auto Insurance
- An insurance coverage that includes liability, collision and a comprehensive insurance policy. Here is an informative guide.
- Full-Depth Reclamation
- A special recycling machine grinds up the roadway, up to 6-10′ deep, and produces a recycled granular base layer, usually incorporating a liquid asphalt emulsion binder. This layer is then paved with one or more layers of asphalt concrete. The finished driving surface could be an asphalt concrete ‘top mix’ or a surface treatment. Since this type of work involves up to three or four layers that often require ‘curing,’ it is usually spread over an 8-12 week period.
- Full dip treatment
- A painting process in which the whole body shell is immersed, used for applying protective Primers
- Full floating
- Mechanism construction in which a shaft is free to turn in all parts in which it is inserted
- Full-floating axle
- A rear drive axle that does not hold the wheel on nor does it hold the wheel in line or support any weight. It merely drives the wheel. Used primarily on racing cars and trucks.
See
- Full-flow oil filter
- An Oil filter that filters all of the oil passing through the engine before it reaches the bearings.
- Full leather
- A car interior in which the door trim, instrument panel, seats are covered in leather
- Full leather upholstery
- A car interior in which the door trim, instrument panel, seats are covered in leather
- Full load
- An engine operating conditions where the accelerator is fully depressed, i.e., the throttle is fully open, which does not necessarily mean high engine speed
See
- Full-load current
- The current drawn from the line when the electric motor is operating at full-load torque and full-load speed at rated frequency and voltage
- Full load enrichment
- The provision of a richer mixture when the throttle is fully opened. On some system, the computer goes open-loop during full-load enrichment
- Full load torque
-
- Maximum torque delivered without overheating.
- The torque necessary to produce the rated horsepower at full-load speed
- Full lock
-
- A condition in which a detachable component (e.g., seat belt buckles) is securely attached.
- The maximum angle attained by the wheels when the steering wheel is turned to its full extent
- Full panel
- A body part that may be made up of several other subassemblies and is fairly complex and cumbersome, e.g., a complete bulkhead assembly incorporating the windshield pillars
- Full respray
- Painting the entire component or entire vehicle as opposed to a partial respray
- Full service history
- (fsh) The documents which show all the work performed on a vehicle, especially the regular service required by the manufacturer
- Full-Size Body
- The body of a bolt or screw which has a diameter between the minimum and maximum limits of the major diameter of the thread.
- Full-size car
- The largest type of car according to the American system. It is a designation no longer used because even full-size cars are now about the size of what was the compact car. In 1970, for instance, a Chevrolet Impala was a full-size car, a Chevelle was an intermediate, and a Nova was a compact. When cars smaller than the Nova came out (i.e., Chevette), they were called sub-compacts.
- Full-size spare
- A spare wheel and tire combination which is the same size as the rest of the wheels. Compare Space saver spare
- Full-skirt piston
- A former piston style which had a full-annulus skirt, without the cutaway section of modern Slipper pistons
- Full sun
- The full sun condition is the amount of power density received at the surface of the earth at noon on a clear day — about 1.0 kilowatt/square-metre. Lower levels of sunlight are often expressed as 0.5 sun or 0.1 sun. A figure of 0.5 sun means that the power density of the sunlight is one-half of that of a full sun.
- Full-time 4×4
- A transmission system on a four-wheeled vehicle in which all four wheels are driven by the engine all the time. Other four-wheel drive units are normally in two-wheel drive mode with four-wheel drive selected by a separate lever when required.
- Full-time four-wheel drive
- A condition where all four wheels are always being driven by the drivetrain. It may include the option of part-time (that is, shifting into 2WD for dry pavement) operation, and may or may not have Hi and Lo 4WD speed ranges. The British term is permanent four-wheel drive.
- Full trailer
- A trailer with axles in the front as well as the rear. It can stand without support. Full trailers are coupled to straight trucks and to the rear of semi or full trailers by a tongue or drawbar. Full trailers are seldom used alone with tractors.
- Full Truckload
- A shipment comprising a full or almost full load on a truck. A full or almost full load is considered to be 39,000 to 44,000 pounds.
- Full-wave rectifier
- A rectifier that converts ac to dc by inverting the negative portion of an ac sine wave.
See
- Fully electronic ignition
- (FEI) A distributorless, mapped ignition system with cylinder-selective knock control, dwell-angle control, and digital idling speed stabilization
- Fully floating axle
- A live rear axle assembly in which the axle shafts serve only to transmit torque to the wheel. The total vehicle weight and cornering loads are transferred directly from the wheel bearings to the axle housing.
- Fully galvanized body
- A body shell which, except for aluminum and plastic parts, is produced entirely of double-sided galvanized steel and galvanized fasteners or which is immersed in galvanizing fluid
- Functional
-
- Capable of working even if it is not working to its peak performance.
- Practical, designed not for esthetics; but solely with a particular use in mind
- Funnel
-
- A cup-shaped object tapering at the bottom to a small hole and a spout, used for pouring oil, fuel, or water into relatively small openings
- A smokestack of a vessel.
- Funny car
- A car equipped with a powerful engine, used for drag racing. Usually has special body (such as Fibreglass) mounted on special lightweight frame and Suspension system.
- Furnace
-
- A heater or large forge for heating plates or shapes for bending
- To bend by heating in furnace.
- Furnace, central warm air
- Self-contained appliance designed to supply heated air through ducts to spaces remote from or adjacent to the appliance location.
- Fuse
-
- A protective electrical device (usually enclosed in glass or plastic) which has a thin wire between two terminals. The wire will break or melt when the current draw exceeds the capacity of the fuse. In this way, the circuit is protected from overload.
- The action of melting when a piece of metal turns to a liquid state and sometimes unites itself to a nearby component.
- A failure of an electrical component because of a blown fuse.
- Fuse box
- A container with a removable cover that holds the fuses for the various electrical circuits, which are all routed through it
- Fuse capacity
-
See
- fuse.
- Fusible link
-
- Special length of smaller gauge wire designed to blow if heavy current flows in circuit
- A wire in the electrical system which outwardly may appear to be no different from other wires, but has a low resistance level so that when the current is above a certain level, the wire melts and breaks continuity.
- Fusible plug
- Plug or fitting made with a metal of a known low-melting temperature. Used as safety device to release pressures in case of fire.
- Fusion fit
- The Adjustable Retention System extending behind a Bell bicycle helmets to allow the helmet to grip your head better.
FVR
Abbreviation for Fuel vapor recovery system
FWD
Abbreviation for Front-wheel drive
FYI
Abbreviation for For Your Information









 Fan
Fan Fastback
Fastback Feeler gauge
Feeler gauge
 Festoon bulb
Festoon bulb F-head engine
F-head engine

 Fifth-wheel travel trailer
Fifth-wheel travel trailer Fifth-wheel trailer
Fifth-wheel trailer File
File Fillister-head machine screw
Fillister-head machine screw Filter wrench
Filter wrench
 Five-door hatchback
Five-door hatchback 1933 Ford with flame paint
1933 Ford with flame paint Flanging tool
Flanging tool Flare nut wrench
Flare nut wrench Flareside Truck
Flareside Truck Flaring tool
Flaring tool Flatbed trailer
Flatbed trailer Flatbed truck
Flatbed truck Flat engine
Flat engine Flat four
Flat four Flathead
Flathead Flathead machine screw
Flathead machine screw Flat-nosed pliers
Flat-nosed pliers Flat Socket Head Cap Screw
Flat Socket Head Cap Screw Flat washer
Flat washer Fleetside
Fleetside
 Flex disc
Flex disc Flex-LocTM
Flex-LocTM Floor jack
Floor jack Floor pump
Floor pump Fluid coupling
Fluid coupling Flywheel
Flywheel Key fob
Key fob Fog light
Fog light Folding camping trailer
Folding camping trailer Greenspan GT3
Greenspan GT3 Fork
Fork Fork lift
Fork lift Formal hardtop
Formal hardtop Formula car
Formula car
 Four bolt mains
Four bolt mains Four-door hardtop
Four-door hardtop Four-door pillared hardtop
Four-door pillared hardtop Four-door sedan
Four-door sedan Four-door station wagon
Four-door station wagon Four-way wheel wrench
Four-way wheel wrench Four-wheel drive
Four-wheel drive Frame
Frame Frame pump
Frame pump Freehub
Freehub Freewheel
Freewheel Front derailleur
Front derailleur Front hub
Front hub Frustum
Frustum Fuel cap
Fuel cap Fuel filter
Fuel filter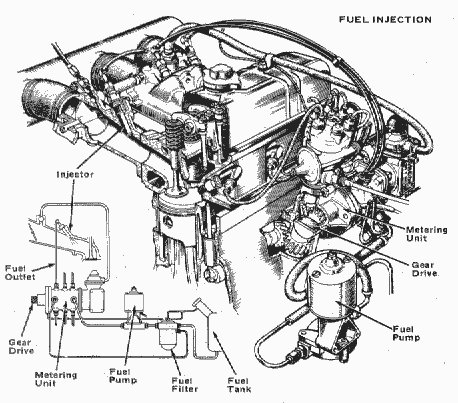 Fuel Injection System
Fuel Injection System Fuel injector
Fuel injector Fuel tank
Fuel tank